Awake Breast Surgery: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 37369489
- PMCID: PMC10347915
- DOI: 10.21873/invivo.13225
Awake Breast Surgery: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background/aim: Awake surgery has become a valid alternative to general anesthesia in many surgery fields. This technique played a very important role during the COVID-19 period. The growing use of this technique has many advantages. We performed a systematic review to study the potentialities of awake breast surgery.
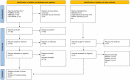
Materials and methods: We searched Pubmed, Embase, and Cochrane library database and retrieved a total of 109 records. Forty-nine of them were excluded as unsuitable. Finally, we selected a total of 12 records concerning different types of studies for topic appropriateness. Three reviewers reviewed independently each record.
Results: Five articles analyzing the sustainability of awake surgery during the COVID-19 period were selected. In addition, one article analyzing the impact on the immune system and six articles and eight case reports analyzing anesthetic techniques were also selected. The studies analyzing awake breast surgery during the COVID-19 period showed advantages in terms of sustainability and length of hospitalization. The study analyzing the immune response after awake breast surgery showed lesser lymphocyte response than the general anesthesia group. The studies analyzing anesthetic techniques in awake breast surgery showed that the nerve blocks allow good level of safety and postoperative pain control.
Conclusion: The awake breast surgery and fast track implementation shortened hospital stays and reduced costs, without influencing the surgical results. Furthermore, awake breast surgery reduced surgical stress compared to general anesthesia. Among the various anesthetic techniques, nerve blocks are the most advantageous in terms of safety and efficacy compared to epidural anesthesia.
Keywords: Awake breast surgery; awake surgery; review; surgery without patient intubation.
Copyright © 2023, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest in relation to this study.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical