Combating Bacterial Biofilms: Current and Emerging Antibiofilm Strategies for Treating Persistent Infections
- PMID: 37370324
- PMCID: PMC10294981
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics12061005
Combating Bacterial Biofilms: Current and Emerging Antibiofilm Strategies for Treating Persistent Infections
Abstract
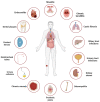
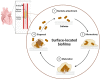
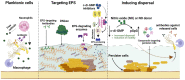
Biofilms are intricate multicellular structures created by microorganisms on living (biotic) or nonliving (abiotic) surfaces. Medically, biofilms often lead to persistent infections, increased antibiotic resistance, and recurrence of infections. In this review, we highlighted the clinical problem associated with biofilm infections and focused on current and emerging antibiofilm strategies. These strategies are often directed at disrupting quorum sensing, which is crucial for biofilm formation, preventing bacterial adhesion to surfaces, impeding bacterial aggregation in viscous mucus layers, degrading the extracellular polymeric matrix, and developing nanoparticle-based antimicrobial drug complexes which target persistent cells within the biofilm core. It is important to acknowledge, however, that the use of antibiofilm agents faces obstacles, such as limited effectiveness in vivo, potential cytotoxicity to host cells, and propensity to elicit resistance in targeted biofilm-forming microbes. Emerging next generation antibiofilm strategies, which rely on multipronged approaches, were highlighted, and these benefit from current advances in nanotechnology, synthetic biology, and antimicrobial drug discovery. The assessment of current antibiofilm mitigation approaches, as presented here, could guide future initiatives toward innovative antibiofilm therapeutic strategies. Enhancing the efficacy and specificity of some emerging antibiofilm strategies via careful investigations, under conditions that closely mimic biofilm characteristics within the human body, could bridge the gap between laboratory research and practical application.
Keywords: antibiofilm agents; antibiofilm nanoparticles; antimicrobial peptides; bacterial biofilm; biofilm infection; quorum sensing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antibiofilm activity of marine microbial natural products: potential peptide- and polyketide-derived molecules from marine microbes toward targeting biofilm-forming pathogens.J Nat Med. 2024 Jan;78(1):1-20. doi: 10.1007/s11418-023-01754-2. Epub 2023 Nov 6. J Nat Med. 2024. PMID: 37930514 Review.
-
Biofilm control strategies in the light of biofilm-forming microorganisms.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Mar 24;39(5):131. doi: 10.1007/s11274-023-03584-6. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36959476 Review.
-
Disruption of Communication: Recent Advances in Antibiofilm Materials with Anti-Quorum Sensing Properties.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Mar 20;16(11):13353-13383. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c01428. Epub 2024 Mar 10. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 38462699 Review.
-
Development of Antibiofilm Therapeutics Strategies to Overcome Antimicrobial Drug Resistance.Microorganisms. 2022 Jan 27;10(2):303. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10020303. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35208758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Strategies to Combat Biofilms Using Antimicrobial Agents and Therapeutic Approaches.Pathogens. 2022 Feb 25;11(3):292. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11030292. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 35335616 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Comprehensive Review on Phage Therapy and Phage-Based Drug Development.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Sep 11;13(9):870. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13090870. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39335043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Public Health Threats Posed by Biofilms and Innovative Strategies for their Control.Discoveries (Craiova). 2024 Dec 31;12(4):e197. doi: 10.15190/d.2024.16. eCollection 2024 Oct-Dec. Discoveries (Craiova). 2024. PMID: 40124593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activity of Synthetic Peptide KP and Its Derivatives against Biofilm-Producing Escherichia coli Strains Resistant to Cephalosporins.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Jul 24;13(8):683. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13080683. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199983 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid Nanocarriers-Enabled Delivery of Antibiotics and Antimicrobial Adjuvants to Overcome Bacterial Biofilms.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Mar 14;16(3):396. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16030396. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38543290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactoferrin Affects the Viability of Bacteria in a Biofilm and the Formation of a New Biofilm Cycle of Mannheimia haemolytica A2.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 9;25(16):8718. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168718. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201405 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

