Inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes Cocktail Culture Biofilms on Crab and Shrimp Coupons and the Expression of Biofilm-Related Genes
- PMID: 37370327
- PMCID: PMC10294894
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics12061008
Inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes Cocktail Culture Biofilms on Crab and Shrimp Coupons and the Expression of Biofilm-Related Genes
Abstract
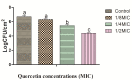
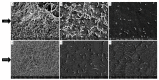
Listeria monocytogenes, a bacterium that is transmitted by tainted food, causes the infection listeriosis. In this study, quercetin was tested for its antibacterial properties and effectiveness as a food additive in preventing the growth of L. monocytogenes cocktail (ATCC19117, ATCC19113, and ATCC15313) biofilms on crabs and shrimps. Quercetin showed the least bactericidal activity and no discernible microbial growth at a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 250 µg/mL. The biofilm inhibition was performed at sub-MICs (1/2, 1/4, and 1/8 MIC). There was no quercetin added to the control group. Additionally, the present work examines the expression of various genes related to biofilm formation and quorum sensing (flaA, fbp, agrA, hlyA, and prfA). The levels of target genes were all significantly down-regulated. Quercetin (0-125 µg/mL) on the surfaces of the crab and shrimp was studied; its inhibitory effects were measured as log reductions at 0.39-2.31 log CFU/cm2 and 0.42-2.36 log CFU/cm2, respectively (p < 0.05). Quercetin reduced the formation of biofilms by disrupting cell-to-cell connections and causing cell lysis, which led to the deformation of the cells, evidenced by FE-SEM (field-emission scanning electron microscopy). These findings emphasize the significance of using natural food agents to target bacteria throughout the entire food production process.
Keywords: Listeria monocytogenes; biofilm; crabs; food safety; quercetin; relative expression; shrimps.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Inhibitory Effect of Quercetin on Biofilm Formation of Listeria monocytogenes Mixed Culture and Repression of Virulence.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Aug 31;11(9):1733. doi: 10.3390/antiox11091733. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139807 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Efficacy of Quercetin against Vibrio parahaemolyticus Biofilm on Food Surfaces and Downregulation of Virulence Genes.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Sep 14;14(18):3847. doi: 10.3390/polym14183847. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36145988 Free PMC article.
-
Control of Listeria monocytogenes in food industry by a combination treatment of natural aromatic compound with Listeria-specific bacteriophage cocktail.Food Res Int. 2024 Feb;177:113859. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2023.113859. Epub 2023 Dec 16. Food Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38225132
-
Inhibition strategies of Listeria monocytogenes biofilms-current knowledge and future outlooks.J Basic Microbiol. 2017 Sep;57(9):728-743. doi: 10.1002/jobm.201700071. Epub 2017 Jun 8. J Basic Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28594071 Review.
-
Listeria monocytogens - Amended understanding of its pathogenesis with a complete picture of its membrane vesicles, quorum sensing, biofilm and invasion.Microb Pathog. 2020 Dec;149:104575. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104575. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Microb Pathog. 2020. PMID: 33091581 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Fucoidan on the Inhibition of Biofilm Formation of Salmonella enterica Subsp. enterica Serovar Typhimurium on Seafoods and Its Molecular Antibiofilm Mechanisms.Microorganisms. 2025 Apr 16;13(4):914. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13040914. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40284748 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hossain M.I., Mizan M.F.R., Roy P.K., Nahar S., Toushik S.H., Ashrafudoulla M., Jahid I.K., Lee J., Ha S.D. Listeria monocytogenes biofilm inhibition on food contact surfaces by application of postbiotics from Lactobacillus curvatus B.67 and Lactobacillus plantarum M.2. Food Res. Int. 2021;148:110595. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110595. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hossain M.I., Kim K., Mizan M.F.R., Toushik S.H., Ashrafudoulla M., Roy P.K., Nahar S., Jahid I.K., Choi C., Park S.H., et al. Comprehensive molecular, probiotic, and quorum-sensing characterization of anti-listerial lactic acid bacteria, and application as bioprotective in a food (milk) model. J. Dairy Sci. 2021;104:6516–6534. doi: 10.3168/jds.2020-19034. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hossain M.I., Mizan M.F.R., Toushik S.H., Roy P.K., Jahid I.K., Park S.H., Ha S.D. Antibiofilm effect of nisin alone and combined with food-grade oil components (thymol and eugenol) against Listeria monocytogenes cocktail culture on food and food-contact surfaces. Food Control. 2022;135:108796. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108796. - DOI
-
- Vazquez-Armenta F.J., Hernandez-Onate M.A., Martinez-Tellez M.A., Lopez-Zavala A.A., Gonzalez-Aguilar G.A., Gutierrez-Pacheco M.M., Ayala-Zavala J.F. Quercetin repressed the stress response factor (sigB) and virulence genes (prfA, actA, inlA, and inlC), lower the adhesion, and biofilm development of L. monocytogenes. Food Microbiol. 2020;87:103377. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2019.103377. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

