Empirical Evidence for the Rescue Effect from a Natural Microcosm
- PMID: 37370418
- PMCID: PMC10295665
- DOI: 10.3390/ani13121907
Empirical Evidence for the Rescue Effect from a Natural Microcosm
Abstract
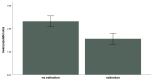
Ecological theory predicts that populations which receive immigrants are less vulnerable to extinction than those that do not receive immigrants (the "rescue effect"). A parallel but opposite process may also exist, where emigration increases the risk of local extinction (the "abandon-ship effect"). Using a natural microcosm of plant-specialist frogs from Madagascar, empirical evidence for both processes is provided. Populations receiving immigrants were less extinction-prone than those without immigration, and those populations losing individuals through emigration were more extinction-prone than those in which no emigration occurred. The number of immigrants and emigrants was also elevated and depressed (respectively) in patches that did not go extinct. These data provide some of the first definitive empirical evidence for the rescue effect and provide suggestive initial data on the abandon-ship effect. Both of these processes may be important to understanding the dynamics of populations.
Keywords: Guibemantis; Pandanus; abandon-ship effect; dispersal; emigration; extinction risk; immigration; population ecology; rescue effect.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Soulé M.E. Introduction. In: Soulé M.E., editor. Viable Populations for Conservation. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, UK: 1987. pp. 1–10.
-
- Harrison S. Local extinction in a metapopulation context: An empirical evaluation. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1991;42:73–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1095-8312.1991.tb00552.x. - DOI
-
- Brown J.H., Kodric-Brown A. Turnover rates in insular biogeography: Effect of immigration on extinction. Ecology. 1977;58:445–449. doi: 10.2307/1935620. - DOI
-
- MacArthur R.H., Wilson E.O. The Theory of Island Biogeography. Princeton University Press; Princeton, NJ, USA: 1967.
-
- Levins R. Some demographic and genetic consequences of environmental heterogeneity for biological control. Am. Entomol. 1969;15:237–240. doi: 10.1093/besa/15.3.237. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

