Exploring the Intersection of Artificial Intelligence and Clinical Healthcare: A Multidisciplinary Review
- PMID: 37370890
- PMCID: PMC10297646
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13121995
Exploring the Intersection of Artificial Intelligence and Clinical Healthcare: A Multidisciplinary Review
Abstract
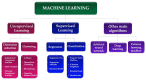
Artificial intelligence (AI) plays a more and more important role in our everyday life due to the advantages that it brings when used, such as 24/7 availability, a very low percentage of errors, ability to provide real time insights, or performing a fast analysis. AI is increasingly being used in clinical medical and dental healthcare analyses, with valuable applications, which include disease diagnosis, risk assessment, treatment planning, and drug discovery. This paper presents a narrative literature review of AI use in healthcare from a multi-disciplinary perspective, specifically in the cardiology, allergology, endocrinology, and dental fields. The paper highlights data from recent research and development efforts in AI for healthcare, as well as challenges and limitations associated with AI implementation, such as data privacy and security considerations, along with ethical and legal concerns. The regulation of responsible design, development, and use of AI in healthcare is still in early stages due to the rapid evolution of the field. However, it is our duty to carefully consider the ethical implications of implementing AI and to respond appropriately. With the potential to reshape healthcare delivery and enhance patient outcomes, AI systems continue to reveal their capabilities.
Keywords: allergology; artificial intelligence; cardiology; dentistry; diagnosis; immunology; machine learning; prediction; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang C., Lu Y. Study on Artificial Intelligence: The State of the Art and Future Prospects. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2021;23:100224. doi: 10.1016/j.jii.2021.100224. - DOI
-
- Muftić F., Kadunić M., Mušinbegović A., Almisreb A.A. Exploring Medical Breakthroughs: A Systematic Review of ChatGPT Applications in Healthcare. Southeast Eur. J. Soft Comput. 2023;12:13–41. doi: 10.21533/scjournal.v12i1.252.g220. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources