Evaluation of Different Registration Algorithms to Reduce Motion Artifacts in CT-Thermography (CTT)
- PMID: 37370971
- PMCID: PMC10296896
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13122076
Evaluation of Different Registration Algorithms to Reduce Motion Artifacts in CT-Thermography (CTT)
Abstract
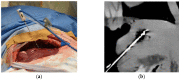
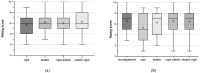
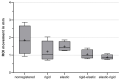
Computed tomography (CT)-based Thermography (CTT) is currently being investigated as a non-invasive temperature monitoring method during ablation procedures. Since multiple CT scans with defined time intervals were acquired during this procedure, interscan motion artifacts can occur between the images, so registration is required. The aim of this study was to investigate different registration algorithms and their combinations for minimizing inter-scan motion artifacts during thermal ablation. Four CTT datasets were acquired using microwave ablation (MWA) of normal liver tissue performed in an in vivo porcine model. During each ablation, spectral CT volume scans were sequentially acquired. Based on initial reconstructions, rigid or elastic registration, or a combination of these, were carried out and rated by 15 radiologists. Friedman's test was used to compare rating results in reader assessments and revealed significant differences for the ablation probe movement rating only (p = 0.006; range, 5.3-6.6 points). Regarding this parameter, readers assessed rigid registration as inferior to other registrations. Quantitative analysis of ablation probe movement yielded a significantly decreased distance for combined registration as compared with unregistered data. In this study, registration was found to have the greatest influence on ablation probe movement, with connected registration being superior to only one registration process.
Keywords: CT; CT thermography; CTT; computed tomography; elastic; registration; rigid; thermoablation.
Conflict of interest statement
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

