GPCR Binding and JNK3 Activation by Arrestin-3 Have Different Structural Requirements
- PMID: 37371033
- PMCID: PMC10296906
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12121563
GPCR Binding and JNK3 Activation by Arrestin-3 Have Different Structural Requirements
Abstract
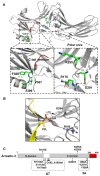
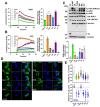
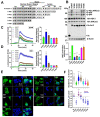
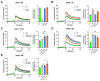
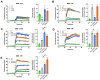
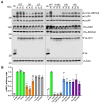
Arrestins bind active phosphorylated G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). Among the four mammalian subtypes, only arrestin-3 facilitates the activation of JNK3 in cells. In available structures, Lys-295 in the lariat loop of arrestin-3 and its homologue Lys-294 in arrestin-2 directly interact with the activator-attached phosphates. We compared the roles of arrestin-3 conformational equilibrium and Lys-295 in GPCR binding and JNK3 activation. Several mutants with enhanced ability to bind GPCRs showed much lower activity towards JNK3, whereas a mutant that does not bind GPCRs was more active. The subcellular distribution of mutants did not correlate with GPCR recruitment or JNK3 activation. Charge neutralization and reversal mutations of Lys-295 differentially affected receptor binding on different backgrounds but had virtually no effect on JNK3 activation. Thus, GPCR binding and arrestin-3-assisted JNK3 activation have distinct structural requirements, suggesting that facilitation of JNK3 activation is the function of arrestin-3 that is not bound to a GPCR.
Keywords: GPCR; JNK3; arrestin; conformation; signaling bias.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Update of
-
GPCR binding and JNK3 activation by arrestin-3 have different structural requirements.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 May 1:2023.05.01.538990. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.01.538990. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Cells. 2023 Jun 06;12(12):1563. doi: 10.3390/cells12121563. PMID: 37205393 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

