Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase as a Therapeutic Target for Alzheimer's Disease and Geriatric Depression
- PMID: 37371332
- PMCID: PMC10296628
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci13060852
Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase as a Therapeutic Target for Alzheimer's Disease and Geriatric Depression
Abstract
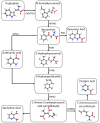
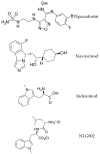
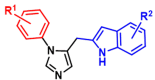
Neuroimmune-triggered neuroinflammation of the central nervous system is emerging as an important aetiopathogenic factor for multiple neurological disorders, including depression, dementia, Alzheimer's disease, multiple sclerosis and others. Tryptophan metabolism via the kynurenic pathway, which is initiated by the indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO-1) enzyme, is a key regulator of the neuroimmune system and its associated neuroinflammatory effects. As discussed in this review, targeting the production of immunopathic and potentially neurotoxic kynurenine metabolites by inhibitory downregulation of IDO-1 may prove a viable target against inflammation-induced neurological conditions, particularly depression and dementia.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; dementia; depression; indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; neuroinflammation; tryptophan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Comai S., Bertazzo A., Brughera M., Crotti S. Chapter Five—Tryptophan in health and disease. In: Makowski G.S., editor. Advances in Clinical Chemistry. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2020. pp. 165–218. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

