Reduced Resting-State EEG Power Spectra and Functional Connectivity after 24 and 36 Hours of Sleep Deprivation
- PMID: 37371427
- PMCID: PMC10296734
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci13060949
Reduced Resting-State EEG Power Spectra and Functional Connectivity after 24 and 36 Hours of Sleep Deprivation
Abstract
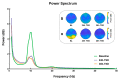
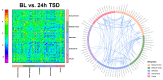
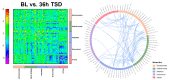
Total sleep deprivation (TSD) leads to cognitive decline; however, the neurophysiological mechanisms underlying resting-state electroencephalogram (EEG) changes after TSD remain unclear. In this study, 42 healthy adult participants were subjected to 36 h of sleep deprivation (36 h TSD), and resting-state EEG data were recorded at baseline, after 24 h of sleep deprivation (24 h TSD), and after 36 h TSD. The analysis of resting-state EEG at baseline, after 24 h TSD, and after 36 h TSD using source localization analysis, power spectrum analysis, and functional connectivity analysis revealed a decrease in alpha-band power and a significant increase in delta-band power after TSD and impaired functional connectivity in the default mode network, precuneus, and inferior parietal lobule. The cortical activities of the precuneus, inferior parietal lobule, and superior parietal lobule were significantly reduced, but no difference was found between the 24 h and 36 h TSD groups. This may indicate that TSD caused some damage to the participants, but this damage temporarily slowed during the 24 h to 36 h TSD period.
Keywords: functional connectivity; power spectrum analysis; resting state; sleep deprivation; source localization analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Reynolds A.C., Banks S. Total sleep deprivation, chronic sleep restriction and sleep disruption. Prog. Brain Res. 2010;185:91–103. - PubMed
-
- Arnal P.J., Sauvet F., Leger D., van Beers P., Bayon V., Bougard C., Rabat A., Millet G.Y., Chennaoui M. Benefits of Sleep Extension on Sustained Attention and Sleep Pressure Before and During Total Sleep Deprivation and Recovery. Sleep. 2015;38:1935–1943. doi: 10.5665/sleep.5244. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

