Transcriptomic Context of RUNX3 Expression in Monocytes: A Cross-Sectional Analysis
- PMID: 37371794
- PMCID: PMC10296263
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11061698
Transcriptomic Context of RUNX3 Expression in Monocytes: A Cross-Sectional Analysis
Abstract
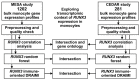
The runt-related transcription factor 3 (RUNX3) regulates the differentiation of monocytes and their response to inflammation. However, the transcriptomic context of RUNX3 expression in blood monocytes remains poorly understood. We aim to learn about RUNX3 from its relationships within transcriptomes of bulk CD14+ cells in adults. This study used immunomagnetically sorted CD14+ cell gene expression microarray data from the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA, n = 1202, GSE56047) and the Correlated Expression and Disease Association Research (CEDAR, n = 281, E-MTAB-6667) cohorts. The data were preprocessed, subjected to RUNX3-focused correlation analyses and random forest modeling, followed by the gene ontology analysis. Immunity-focused differential ratio analysis with intermediary inference (DRAIMI) was used to integrate the data with protein-protein interaction network. Correlation analysis of RUNX3 expression revealed the strongest positive association for EVL (rmean = 0.75, pFDR-MESA = 5.37 × 10-140, pFDR-CEDAR = 5.52 × 10-80), ARHGAP17 (rmean = 0.74, pFDR-MESA = 1.13 × 10-169, pFDR-CEDAR = 9.20 × 10-59), DNMT1 (rmean = 0.74, pFDR-MESA = 1.10 × 10-169, pFDR-CEDAR = 1.67 × 10-58), and CLEC16A (rmean = 0.72, pFDR-MESA = 3.51 × 10-154, pFDR-CEDAR = 2.27 × 10-55), while the top negative correlates were C2ORF76 (rmean = -0.57, pFDR-MESA = 8.70 × 10-94, pFDR-CEDAR = 1.31 × 10-25) and TBC1D7 (rmean = -0.55, pFDR-MESA = 1.36 × 10-69, pFDR-CEDAR = 7.81 × 10-30). The RUNX3-associated transcriptome signature was involved in mRNA metabolism, signal transduction, and the organization of cytoskeleton, chromosomes, and chromatin, which may all accompany mitosis. Transcriptomic context of RUNX3 expression in monocytes hints at its relationship with cell growth, shape maintenance, and aspects of the immune response, including tyrosine kinases.
Keywords: RUNX3 expression; immunity; inflammation; monocyte; transcriptome.
Conflict of interest statement
E.D. declares no conflict of interest related to this study. J.K.N. reports personal fees from Norsa Pharma, grant support from the Biocodex Microbiota Foundation, outside of the submitted work. J.W. reports personal fees and nonfinancial support from Biocodex, BGP Products, Chiesi, Hipp, Humana, Mead Johnson Nutrition, Merck Sharp and Dohme, Nestle, Norsa Pharma, Nutricia, Roche, Sequoia Pharmaceuticals, and Vitis Pharma, outside the submitted work, as well as grants, personal fees, and nonfinancial support from Nutricia Research Foundation Poland, also outside the submitted work.
References
-
- Adams A.T., Kennedy N.A., Hansen R., Ventham N.T., O’Leary K.R., Drummond H.E., Noble C.L., El-Omar E., Russell R.K., Wilson D.C., et al. Two-Stage Genome-Wide Methylation Profiling in Childhood-Onset Crohn’s Disease Implicates Epigenetic Alterations at the VMP1/MIR21 and HLA Loci. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2014;20:1784–1793. doi: 10.1097/MIB.0000000000000179. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials