Lady's Bedstraw as a Powerful Antioxidant for Attenuation of Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity
- PMID: 37372007
- PMCID: PMC10295214
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12061277
Lady's Bedstraw as a Powerful Antioxidant for Attenuation of Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity
Abstract
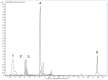
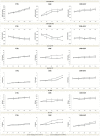
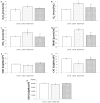
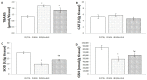
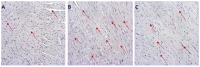
This study aimed to examine the effects of a 14-day treatment with lady's bedstraw methanol extract on doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity through functional, biochemical and histological examinations. We used 24 male Wistar albino rats divided into the following groups: control (CTRL), doxorubicin (DOX), and DOX + GVE (Galium verum extract). GVE was administered orally at a dose of 50 mg/kg per day for 14 days, while a single dose of doxorubicin was injected into the DOX groups. After accomplishing treatment with GVE, cardiac function was assessed, which determined the redox state. During the autoregulation protocol on the Langendorff apparatus, ex vivo cardiodynamic parameters were measured. Our results demonstrated that the consumption of GVE effectively suppressed the disturbed response of the heart to changes in perfusion pressures caused by administration of DOX. Intake of GVE was associated with a reduction in most of the measured prooxidants in comparison to the DOX group. Moreover, this extract was capable of increasing the activity of the antioxidant defense system. Morphometric analyses showed that rat hearts treated with DOX showed more pronounced degenerative changes and necrosis compared to the CTRL group. However, GVE pretreatment seems to be able to prevent the pathological injuries caused by DOX injection via decrease in oxidative stress and apoptosis.
Keywords: cardiac function; doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity; lady’s bedstraw; oxidative stress; rat.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Sergazy S., Shulgau Z., Fedotovskikh G., Chulenbayeva L., Nurgozhina A., Nurgaziyev M., Krivyh E., Kamyshanskiy Y., Kushugulova A., Gulyayev A., et al. Cardioprotective effect of grape polyphenol extract against doxorubicin induced cardiotoxicity. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:14720. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-71827-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bradic J., Zivkovic V., Srejovic I., Jakovljevic V., Petkovic A., Turnic T.N., Jeremic J., Jeremic N., Mitrovic S., Sobot T., et al. Protective Effects of Galium verum L. Extract against Cardiac Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019;2019:4235405. doi: 10.1155/2019/4235405. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zaichikova S.G., Bokov D.O., Kiselevskii M.V., Antsyshkina A.M., Bondar A.A., Prostodusheva T.V., Shchepochkina OYu Gegechkori V.I. Determination of the Chemical Composition of Lady’s Bedstraw (Galium verum L.) Herb Extract by GC-MS. Pharmacogn. J. 2020;12:857–863. doi: 10.5530/pj.2020.12.123. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

