Computational Characterization of the Binding Properties of the HIV1-Neutralizing Antibody PG16 and Design of PG16-Derived CDRH3 Peptides
- PMID: 37372110
- PMCID: PMC10295463
- DOI: 10.3390/biology12060824
Computational Characterization of the Binding Properties of the HIV1-Neutralizing Antibody PG16 and Design of PG16-Derived CDRH3 Peptides
Abstract
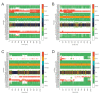
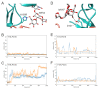
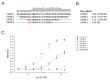
PG16 is a broadly neutralizing antibody that binds to the gp120 subunit of the HIV-1 Env protein. The major interaction site is formed by the unusually long complementarity determining region (CDR) H3. The CDRH3 residue Tyr100H is known to represent a tyrosine sulfation site; however, this modification is not present in the experimental complex structure of PG16 with full-length HIV-1 Env. To investigate the role of sulfation for this complex, we modeled the sulfation of Tyr100H and compared the dynamics and energetics of the modified and unmodified complex by molecular dynamics simulations at the atomic level. Our results show that sulfation does not affect the overall conformation of CDRH3, but still enhances gp120 interactions both at the site of modification and for the neighboring residues. This stabilization affects not only protein-protein contacts, but also the interactions between PG16 and the gp120 glycan shield. Furthermore, we also investigated whether PG16-CDRH3 is a suitable template for the development of peptide mimetics. For a peptide spanning residues 93-105 of PG16, we obtained an experimental EC50 value of 3nm for the binding of gp120 to the peptide. This affinity can be enhanced by almost one order of magnitude by artificial disulfide bonding between residues 99 and 100F. In contrast, any truncation results in significantly lower affinity, suggesting that the entire peptide segment is involved in gp120 recognition. Given their high affinity, it should be possible to further optimize the PG16-derived peptides as potential inhibitors of HIV invasion.
Keywords: HIV-1; PG16; antibody; antibody mimetic peptides; molecular dynamics; peptides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Structure and function of broadly reactive antibody PG16 reveal an H3 subdomain that mediates potent neutralization of HIV-1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jun 22;107(25):11483-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1004600107. Epub 2010 Jun 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20534513 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a remote mutation from the contact paratope on the structure of CDR-H3 in the anti-HIV neutralizing antibody PG16.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 27;9(1):19840. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56154-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31882602 Free PMC article.
-
Trimeric gp120-specific bovine monoclonal antibodies require cysteine and aromatic residues in CDRH3 for high affinity binding to HIV Env.MAbs. 2017 Apr;9(3):550-566. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2016.1270491. Epub 2016 Dec 20. MAbs. 2017. PMID: 27996375 Free PMC article.
-
Potent and broad anti-HIV-1 activity exhibited by a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-anchored peptide derived from the CDR H3 of broadly neutralizing antibody PG16.J Virol. 2011 Sep;85(17):8467-76. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00520-11. Epub 2011 Jun 29. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21715497 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody responses to the HIV-1 envelope high mannose patch.Adv Immunol. 2019;143:11-73. doi: 10.1016/bs.ai.2019.08.002. Epub 2019 Sep 11. Adv Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31607367 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tyrosine Sulfation at Antibody Light Chain CDR-1 Increases Binding Affinity and Neutralization Potency to Interleukine-4.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 5;25(3):1931. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031931. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38339208 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J.C., Rey F., Nugeyre M.T., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Dauguet C., Axler-Blin C., Vézinet-Brun F., Rouzioux C., et al. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) Science. 1983;220:868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6189183. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gallo R.C., Salahuddin S.Z., Popovic M., Shearer G.M., Kaplan M., Haynes B.F., Palker T.J., Redfield R., Oleske J., Safai B., et al. Frequent detection and isolation of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and at risk for AIDS. Science. 1984;224:500–503. doi: 10.1126/science.6200936. - DOI - PubMed
-
- UNAIDS Homepage—unaids.org. 2023. [(accessed on 23 April 2023)]. Available online: https://www.unaids.org/en.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

