Complex/cryptic EWSR1::FLI1/ERG Gene Fusions and 1q Jumping Translocation in Pediatric Ewing Sarcomas
- PMID: 37372318
- PMCID: PMC10298448
- DOI: 10.3390/genes14061139
Complex/cryptic EWSR1::FLI1/ERG Gene Fusions and 1q Jumping Translocation in Pediatric Ewing Sarcomas
Abstract
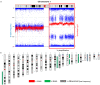
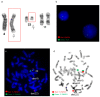
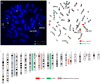
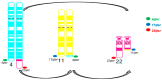
Ewing sarcomas (ES) are rare small round cell sarcomas often affecting children and characterized by gene fusions involving one member of the FET family of genes (usually EWSR1) and a member of the ETS family of transcription factors (usually FLI1 or ERG). The detection of EWSR1 rearrangements has important diagnostic value. Here, we conducted a retrospective review of 218 consecutive pediatric ES at diagnosis and found eight patients having data from chromosome analysis, FISH/microarray, and gene-fusion assay. Three of these eight ES had novel complex/cryptic EWSR1 rearrangements/fusions by chromosome analysis. One case had a t(9;11;22)(q22;q24;q12) three-way translocation involving EWSR1::FLI1 fusion and 1q jumping translocation. Two cases had cryptic EWSR1 rearrangements/fusions, including one case with a cryptic t(4;11;22)(q35;q24;q12) three-way translocation involving EWSR1::FLI1 fusion, and the other had a cryptic EWSR1::ERG rearrangement/fusion on an abnormal chromosome 22. All patients in this study had various aneuploidies with a gain of chromosome 8 (75%), the most common, followed by a gain of chromosomes 20 (50%) and 4 (37.5%), respectively. Recognition of complex and/or cryptic EWSR1 gene rearrangements/fusions and other chromosome abnormalities (such as jumping translocation and aneuploidies) using a combination of various genetic methods is important for accurate diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment outcomes of pediatric ES.
Keywords: 1q jumping translocation; EWSR1::ERG gene fusion; EWSR1::FLI1 gene fusions; Ewing sarcomas; cryptic translocation; three-way translocation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



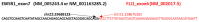
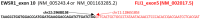


References
-
- The WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board . WHO Classification of Tumours Soft Tissue and Bone Tumours. 5th ed. IARC Press; Lyon, France: 2020.
-
- Sandberg A.A., Bridge J.A. The Cytogenetics of Bone and Soft Tissue Tumors. R.G.; Austin, TX, USA: Landes, France: 1994. p. 469.
-
- Turc-Carel C., Aurias A., Mugneret F., Lizard S., Sidaner I., Volk C., Thiery J.P., Olschwang S., Philip I., Berger M.P., et al. Chromosomes in Ewing’s sarcoma. I. An evaluation of 85 cases of remarkable consistency of t(11;22)(q24;q12) Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 1988;32:229–238. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(88)90285-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Delattre O., Zucman J., Melot T., Garau X.S., Zucker J.-M., Lenoir G.M., Ambros P.F., Sheer D., Turc-Carel C., Triche T.J., et al. The Ewing Family of Tumors—A Subgroup of Small-Round-Cell Tumors Defined by Specific Chimeric Transcripts. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994;331:294–299. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199408043310503. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ohno T., Rao V.N., Reddy E.S. EWS/Fli-1 chimeric protein is a transcriptional activator. Cancer Res. 1993;53:5859–5863. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

