Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A thorough Bioinformatic Analysis of Gene Expression and Clinical Data
- PMID: 37372430
- PMCID: PMC10298340
- DOI: 10.3390/genes14061250
Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A thorough Bioinformatic Analysis of Gene Expression and Clinical Data
Abstract
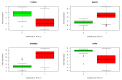
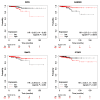
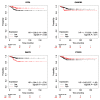
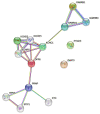
The likelihood of being diagnosed with thyroid cancer has increased in recent years; it is the fastest-expanding cancer in the United States and it has tripled in the last three decades. In particular, Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma (PTC) is the most common type of cancer affecting the thyroid. It is a slow-growing cancer and, thus, it can usually be cured. However, given the worrying increase in the diagnosis of this type of cancer, the discovery of new genetic markers for accurate treatment and prognostic is crucial. In the present study, the aim is to identify putative genes that may be specifically relevant in PTC through bioinformatic analysis of several gene expression public datasets and clinical information. Two datasets from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) dataset were studied. Statistics and machine learning methods were sequentially employed to retrieve a final small cluster of genes of interest: PTGFR, ZMAT3, GABRB2, and DPP6. Kaplan-Meier plots were employed to assess the expression levels regarding overall survival and relapse-free survival. Furthermore, a manual bibliographic search for each gene was carried out, and a Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI) network was built to verify existing associations among them, followed by a new enrichment analysis. The results revealed that all the genes are highly relevant in the context of thyroid cancer and, more particularly interesting, PTGFR and DPP6 have not yet been associated with the disease up to date, thus making them worthy of further investigation as to their relationship to PTC.
Keywords: GEO; RNA-seq gene expression data; TCGA; gene expression analysis; microarray gene expression data; statistical learning; thyroid cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Rao M.S., Van Vleet T.R., Ciurlionis R., Buck W.R., Mittelstadt S.W., Blomme E.A.G., Liguori M.J. Comparison of RNA-Seq and Microarray Gene Expression Platforms for the Toxicogenomic Evaluation of Liver From Short-Term Rat Toxicity Studies. Front. Genet. 2019;9:636. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00636. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

