Immunomodulatory Role of Interferons in Viral and Bacterial Infections
- PMID: 37373262
- PMCID: PMC10298684
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241210115
Immunomodulatory Role of Interferons in Viral and Bacterial Infections
Abstract
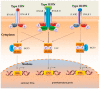
Interferons are a group of immunomodulatory substances produced by the human immune system in response to the presence of pathogens, especially during viral and bacterial infections. Their remarkably diverse mechanisms of action help the immune system fight infections by activating hundreds of genes involved in signal transduction pathways. In this review, we focus on discussing the interplay between the IFN system and seven medically important and challenging viruses (herpes simplex virus (HSV), influenza, hepatitis C virus (HCV), lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), and SARS-CoV coronavirus) to highlight the diversity of viral strategies. In addition, the available data also suggest that IFNs play an important role in the course of bacterial infections. Research is currently underway to identify and elucidate the exact role of specific genes and effector pathways in generating the antimicrobial response mediated by IFNs. Despite the numerous studies on the role of interferons in antimicrobial responses, many interdisciplinary studies are still needed to understand and optimize their use in personalized therapeutics.
Keywords: Epstein–Barr virus; IFN-α; IFN-β; IFN-γ; SARS-CoV coronavirus; bacterial infections; hepatitis C virus; herpes simplex virus; immune system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

