Genome-Wide Analysis of Strictosidine Synthase-like Gene Family Revealed Their Response to Biotic/Abiotic Stress in Poplar
- PMID: 37373265
- PMCID: PMC10298878
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241210117
Genome-Wide Analysis of Strictosidine Synthase-like Gene Family Revealed Their Response to Biotic/Abiotic Stress in Poplar
Abstract
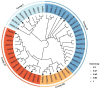
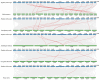
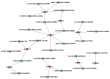
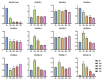
The strictosidine synthase-like (SSL) gene family is a small plant immune-regulated gene family that plays a critical role in plant resistance to biotic/abiotic stresses. To date, very little has been reported on the SSL gene in plants. In this study, a total of thirteen SSLs genes were identified from poplar, and these were classified into four subgroups based on multiple sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree analysis, and members of the same subgroup were found to have similar gene structures and motifs. The results of the collinearity analysis showed that poplar SSLs had more collinear genes in the woody plants Salix purpurea and Eucalyptus grandis. The promoter analysis revealed that the promoter region of PtrSSLs contains a large number of biotic/abiotic stress response elements. Subsequently, we examined the expression patterns of PtrSSLs following drought, salt, and leaf blight stress, using RT-qPCR to validate the response of PtrSSLs to biotic/abiotic stresses. In addition, the prediction of transcription factor (TF) regulatory networks identified several TFs, such as ATMYB46, ATMYB15, AGL20, STOP1, ATWRKY65, and so on, that may be induced in the expression of PtrSSLs in response to adversity stress. In conclusion, this study provides a solid basis for a functional analysis of the SSL gene family in response to biotic/abiotic stresses in poplar.
Keywords: Populus trichocarpa; SSL; STR; Strictosidine synthase; family; stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Genome-Wide Characterization of the BTB Gene Family in Poplar and Expression Analysis in Response to Hormones and Biotic/Abiotic Stresses.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 21;25(16):9048. doi: 10.3390/ijms25169048. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201733 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of SIMILAR TO RCD ONE (SRO) Family Revealed Their Roles in Abiotic Stress in Poplar.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 19;24(4):4146. doi: 10.3390/ijms24044146. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835559 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of Aquaporins Gene Family in Populus euphratica and Its Expression Patterns in Response to Drought, Salt Stress, and Phytohormones.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 23;25(18):10185. doi: 10.3390/ijms251810185. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337672 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of Multiple Organellar RNA Editing Factor Family in Poplar Reveals Evolution and Roles in Drought Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 21;20(6):1425. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061425. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30901839 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide expression analysis of phospholipase A1 (PLA1) gene family suggests phospholipase A1-32 gene responding to abiotic stresses in cotton.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Dec 1;192:1058-1074. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.10.038. Epub 2021 Oct 14. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 34656543 Review.
Cited by
-
The Genome-Wide Identification, Characterization, and Expression Analysis of the Strictosidine Synthase-like Family in Maize (Zea mays L.).Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 29;24(19):14733. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914733. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834181 Free PMC article.
-
Post-polyploidization centromere evolution in cotton.Nat Genet. 2025 Apr;57(4):1021-1030. doi: 10.1038/s41588-025-02115-3. Epub 2025 Mar 3. Nat Genet. 2025. PMID: 40033059
-
Co-Expression Network Analysis and Introgressive Gene Identification for Fiber Length and Strength Reveal Transcriptional Differences in 15 Cotton Chromosome Substitution Segment Lines and Their Upland and Sea Island Parents.Plants (Basel). 2024 Aug 19;13(16):2308. doi: 10.3390/plants13162308. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204744 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative proteomic analysis based on TMT reveals different responses of Haloxylon ammodendron and Haloxylon persicum to long-term drought.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Apr 15;25(1):480. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06513-x. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40234745 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis of resistant and susceptible Medicago truncatula genotypes in response to spring black stem and leaf spot disease.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Jul 29;24(1):720. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05444-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 39075348 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

