Extracellular Vesicles as Drug Transporters
- PMID: 37373411
- PMCID: PMC10299356
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241210267
Extracellular Vesicles as Drug Transporters
Abstract
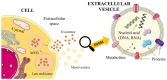
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are lipid bilayer-delimited particles. According to their size and synthesis pathway, EVs can be classified into exosomes, ectosomes (microvesicles), and apoptotic bodies. Extracellular vesicles are of great interest to the scientific community due to their role in cell-to-cell communication and their drug-carrying abilities. The study aims to show opportunities for the application of EVs as drug transporters by considering techniques applicable for loading EVs, current limitations, and the uniqueness of this idea compared to other drug transporters. In addition, EVs have therapeutic potential in anticancer therapy (especially in glioblastoma, pancreatic cancer, and breast cancer).
Keywords: cancer treatment; drug delivery; engineering; extracellular vesicles; nanomedicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Foster B.P., Balassa T., Benen T.D., Dominovic M., Elmadjian G.K., Florova V., Fransolet M.D., Kestlerova A., Kmiecik G., Kostadinova I.A., et al. Extracellular vesicles in blood, milk and body fluids of the female and male urogenital tract and with special regard to reproduction. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2016;53:379–395. doi: 10.1080/10408363.2016.1190682. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources