Hyaluronic Acid: A Powerful Biomolecule with Wide-Ranging Applications-A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 37373443
- PMCID: PMC10299688
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241210296
Hyaluronic Acid: A Powerful Biomolecule with Wide-Ranging Applications-A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
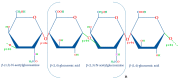
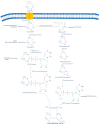
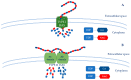
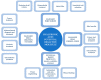
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a glycosaminoglycan widely distributed in the human body, especially in body fluids and the extracellular matrix of tissues. It plays a crucial role not only in maintaining tissue hydration but also in cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, and the inflammatory response. HA has demonstrated its efficacy as a powerful bioactive molecule not only for skin antiaging but also in atherosclerosis, cancer, and other pathological conditions. Due to its biocompatibility, biodegradability, non-toxicity, and non-immunogenicity, several HA-based biomedical products have been developed. There is an increasing focus on optimizing HA production processes to achieve high-quality, efficient, and cost-effective products. This review discusses HA's structure, properties, and production through microbial fermentation. Furthermore, it highlights the bioactive applications of HA in emerging sectors of biomedicine.
Keywords: bioactive molecule; biomaterial; bioproduction; fermentation processes; hyaluronic acid; metabolic pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Li Z., Tao L., Yinhong X., Zheng Z., Junying C. A new classification method of nanotechnology for design integration in biomaterials. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2020;9:820–832. doi: 10.1515/ntrev-2020-0063. - DOI
-
- Kandasamy G., Annenkov V., Krishnan U.M. Nanoimmunotherapy—Cloaked defenders to breach the cancer fortress. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2018;7:317–340. doi: 10.1515/ntrev-2018-0013. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

