Pathogenic Role of IL-17 and Therapeutic Targeting of IL-17F in Psoriatic Arthritis and Spondyloarthropathies
- PMID: 37373452
- PMCID: PMC10299014
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241210305
Pathogenic Role of IL-17 and Therapeutic Targeting of IL-17F in Psoriatic Arthritis and Spondyloarthropathies
Abstract
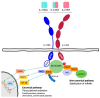
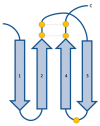
The interleukin 17 (IL-17) family, a subset of cytokines consisting of IL-17A-F, plays crucial roles in host defence against microbial organisms and the development of inflammatory diseases, including psoriasis (PsO), axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA), and psoriatic arthritis (PsA). IL-17A is the signature cytokine produced by T helper 17 (Th17) cells and is considered the most biologically active form. The pathogenetic involvement of IL-17A in these conditions has been confirmed, and its blockade with biological agents has provided a highly effective therapeutical approach. IL-17F is also overexpressed in the skin and synovial tissues of patients with these diseases, and recent studies suggest its involvement in promoting inflammation and tissue damage in axSpA and PsA. The simultaneous targeting of IL-17A and IL-17F by dual inhibitors and bispecific antibodies may improve the management of Pso, PsA, and axSpA, as demonstrated in the pivotal studies of dual specific antibodies such as bimekizumab. The present review focuses on the role of IL-17F and its therapeutic blockade in axSpA and PsA.
Keywords: axial spondyloarthritis; bimekizumab; interleukin 17F; psoriasis; psoriatic arthritis; sonelokimab.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

