Atorvastatin and Fluvastatin Potentiate Blood Pressure Lowering Effect of Amlodipine through Vasorelaxant Phenomenon
- PMID: 37374229
- PMCID: PMC10303907
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina59061023
Atorvastatin and Fluvastatin Potentiate Blood Pressure Lowering Effect of Amlodipine through Vasorelaxant Phenomenon
Abstract
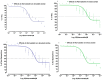
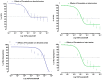
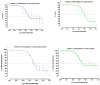
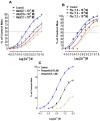
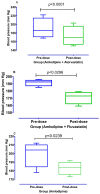
Background and Objectives: We have recently reported that stains have calcium channel blocking activity in isolated jejunal preparations. In this study, we examined the effects of atorvastatin and fluvastatin on blood vessels for a possible vasorelaxant effect. We also studied the possible additional vasorelaxant effect of atorvastatin and fluvastatin, in the presence of amlodipine, to quantify its effects on the systolic blood pressure of experimental animals. Materials and Methods: Atorvastatin and fluvastatin were tested in isolated rabbits' aortic strip preparations using 80mM Potassium Chloride (KCl) induced contractions and 1 micro molar Norepinephrine (NE) induced contractions. A positive relaxing effect on 80 mM KCl induced contractions were further confirmed in the absence and presence of atorvastatin and fluvastatin by constructing calcium concentration response curves (CCRCs) while using verapamil as a standard calcium channel blocker. In another series of experiments, hypertension was induced in Wistar rats and different test concentrations of atorvastatin and fluvastatin were administered in their respective EC50 values to the test animals. A fall in their systolic blood pressure was noted using amlodipine as a standard vasorelaxant drug. Results: The results show that fluvastatin is more potent than amlodipine as it relaxed NE induced contractions where the amplitude reached 10% of its control in denuded aortae. Atorvastatin relaxed KCL induced contractions with an amplitude reaching 34.4% of control response as compared to the amlodipine response, i.e., 39.1%. A right shift in the EC50 (Log Ca++ M) of Calcium Concentration Response Curves (CCRCs) implies that statins have calcium channel blocking activity. A right shift in the EC50 of fluvastatin with relatively less EC50 value (-2.8 Log Ca++ M) in the presence of test concentration (1.2 × 10-7 M) of fluvastatin implies that fluvastatin is more potent than atorvastatin. The shift in EC50 resembles the shift of Verapamil, a standard calcium channel blocker (-1.41 Log Ca++ M). Conclusions: Atorvastatin and fluvastatin relax the aortic strip preparations predominantly through the inhibition of voltage gated calcium channels in high molar KCL induced contractions. These statins also inhibit the effects of NE induced contractions. The study also confirms that atorvastatin and fluvastatin potentiate blood pressure lowering effects in hypertensive rats.
Keywords: amlodipine; atorvastatin; calcium channel blocking activity; fluvastatin; statins; verapamil.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pitavastatin and Lovastatin Exhibit Calcium Channel Blocking Activity Which Potentiate Vasorelaxant Effects of Amlodipine: A New Futuristic Dimension in Statin's Pleiotropy.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Oct 10;59(10):1805. doi: 10.3390/medicina59101805. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37893523 Free PMC article.
-
Current statins show calcium channel blocking activity through voltage gated channels.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2016 Sep 21;17(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s40360-016-0086-5. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27649899 Free PMC article.
-
Rosuvastatin and Simvastatin potentiate antihypertensive effect of amlodipine through vasorelaxation phenomenon.Pak J Pharm Sci. 2023 May;36(3(Special)):953-961. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2023. PMID: 37587704
-
Amlodipine and atorvastatin in atherosclerosis: a review of the potential of combination therapy.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2004 Feb;5(2):459-68. doi: 10.1517/14656566.5.2.459. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2004. PMID: 14996641 Review.
-
A single-pill combination of amlodipine besylate and atorvastatin calcium.Drugs Today (Barc). 2006 Mar;42(3):157-75. doi: 10.1358/dot.2006.42.3.953593. Drugs Today (Barc). 2006. PMID: 16628258 Review.
Cited by
-
New Lead Schiff Bases Predominantly Mediate Vasorelaxant Activity Through α1 Receptor Blocking Activity.Biomolecules. 2025 Apr 23;15(5):611. doi: 10.3390/biom15050611. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40427504 Free PMC article.
-
Safety of combined drug use in patients with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases: an analysis based on the spontaneous reporting database of adverse drug reactions in Hubei Province.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 8;15:1451713. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1451713. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39845792 Free PMC article.
-
Pitavastatin and Lovastatin Exhibit Calcium Channel Blocking Activity Which Potentiate Vasorelaxant Effects of Amlodipine: A New Futuristic Dimension in Statin's Pleiotropy.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Oct 10;59(10):1805. doi: 10.3390/medicina59101805. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37893523 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Organization WHO Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs) Fact Sheet. no 317. 2012. 2014. [(accessed on 1 April 2023)]. Available online: https://aho.org/fact-sheets/cardiovascular-diseases-cvds-fact-sheet/
-
- Joseph P., Kutty V.R., Mohan V., Kumar R., Mony P., Vijayakumar K., Islam S., Iqbal R., Kazmi K., Rahman O., et al. Cardiovascular disease, mortality, and their associations with modifiable risk factors in a multi-national South Asia cohort: A PURE substudy. Eur. Hear. J. 2022;43:2831–2840. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac249. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mensah G.A., Roth G.A., Fuster V. The Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors: 2020 and Beyond. American College of Cardiology Foundation; Washington, DC, USA: 2019. pp. 2529–2532. - PubMed
-
- Margolis K.L., Davis B.R., Baimbridge C., Ciocon J.O., Cuyjet A.B., Dart R.A., Einhorn P.T., Ford C.E., Gordon D., Hartney T.J., et al. Long-Term Follow-Up of Moderately Hypercholesterolemic Hypertensive Patients Following Randomization to Pravastatin vs. Usual Care: The Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT-LLT) J. Clin. Hypertens. 2013;15:542–554. doi: 10.1111/jch.12139. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Neutel J.M., Bestermann W.H., Dyess E.M., Alan G., Attila K., Santosh S., Carla Y. The use of a single-pill calcium channel blocker/statin combination in the management of hypertension and dyslipidemia: A randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter study. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2009;11:22–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2008.00058.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

