Effects of Heterogenization Treatment on the Hot-Working Temperature and Mechanical Properties of Al-Cu-Mg-Mn-(Zr) Alloys
- PMID: 37374443
- PMCID: PMC10301225
- DOI: 10.3390/ma16124256
Effects of Heterogenization Treatment on the Hot-Working Temperature and Mechanical Properties of Al-Cu-Mg-Mn-(Zr) Alloys
Abstract
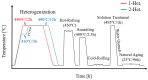
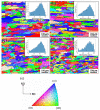
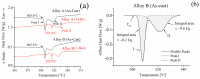
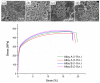
This study investigated the effects of a minor Zr addition (0.15 wt%) and heterogenization treatment (one-stage/two-stage) on the hot-working temperature and mechanical properties in Al-4.9Cu-1.2Mg-0.9Mn alloy. The results indicated that the eutectic phases (α-Al + θ-Al2Cu + S-Al2CuMg) dissolved after heterogenization, retaining θ-Al2Cu and τ1-Al29Cu4Mn6 phases, while the onset melting temperature increased to approximately 17 °C. A change in the onset melting temperature and evolution of the microstructure is used to assess an improvement in hot-working behavior. With the minor Zr addition, the alloy exhibited enhanced mechanical properties due to grain growth inhibition. Zr-added alloys show 490 ± 3 MPa ultimate tensile strength and 77.5 ± 0.7 HRB hardness after T4 tempering, compared to 460 ± 2.2 MPa and 73.7 ± 0.4 HRB for un-added alloys. Additionally, combining minor Zr addition and two-stage heterogenization resulted in finer Al3Zr dispersoids. Two-stage heterogenized alloys had an average Al3Zr size of 15 ± 5 nm, while one-stage heterogenized alloys had an average size of 25 ± 8 nm. A partial decrease in the mechanical properties of the Zr-free alloy was observed after two-stage heterogenization. The one-stage heterogenized alloy had 75.4 ± 0.4 HRB hardness after being T4-tempered, whereas the two-stage heterogenized alloy had 73.7 ± 0.4 HRB hardness after being T4-tempered.
Keywords: Al-Cu-Mg-Mn alloy; Al3Zr; heterogenization; melting temperature; zirconium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Warner T. Recently-developed aluminum solutions for aerospace applications. Mater. Sci. 2006;519:1271–1278.
-
- Saha P.K. Aluminum Extrusion Technology. ASM International; Materials Park, OH, USA: 2000.
-
- Wang J., Xiao X. Thermodynamic and Kinetic Calculation of High Strength Aluminum-Lithium Alloy. Crystals. 2022;12:472. doi: 10.3390/cryst12040472. - DOI
-
- Wang L., Strangwood M., Balinta D., Lin J., Dean T.A. Formability and failure mechanisms of AA2024 under hot forming conditions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2011;197:2648–2656. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2010.11.084. - DOI
-
- Xu X.F., Zhao Y.G. Rapid grain refinement of AA2024 alloy through recrystallization induced by electro-pulsing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2014;612:223–226. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2014.06.057. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

