Oral and Topical Probiotics and Postbiotics in Skincare and Dermatological Therapy: A Concise Review
- PMID: 37374920
- PMCID: PMC10301930
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11061420
Oral and Topical Probiotics and Postbiotics in Skincare and Dermatological Therapy: A Concise Review
Abstract
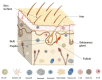
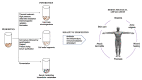
The skin microbiota is a pivotal contributor to the maintenance of skin homeostasis by protecting it from harmful pathogens and regulating the immune system. An imbalance in the skin microbiota can lead to pathological conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, and acne. The balance of the skin microbiota components can be disrupted by different elements and dynamics such as changes in pH levels, exposure to environmental toxins, and the use of certain skincare products. Some research suggests that certain probiotic strains and their metabolites (postbiotics) may provide benefits such as improving the skin barrier function, reducing inflammation, and improving the appearance of acne-prone or eczema-prone skin. Consequently, in recent years probiotics and postbiotics have become a popular ingredient in skincare products. Moreover, it was demonstrated that skin health can be influenced by the skin-gut axis, and imbalances in the gut microbiome caused by poor diet, stress, or the use of antibiotics can lead to skin conditions. In this way, products that improve gut microbiota balance have been gaining attention from cosmetic and pharmaceutical companies. The present review will focus on the crosstalk between the SM and the host, and its effects on health and diseases.
Keywords: oral; postbiotics; probiotics; skin; skincare; topical.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources