Recent Advances in Two-Dimensional MXene-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Sweat Analysis
- PMID: 37375172
- PMCID: PMC10303649
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28124617
Recent Advances in Two-Dimensional MXene-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Sweat Analysis
Abstract
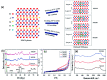
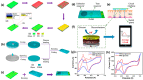
Sweat, a biofluid secreted naturally from the eccrine glands of the human body, is rich in several electrolytes, metabolites, biomolecules, and even xenobiotics that enter the body through other means. Recent studies indicate a high correlation between the analytes' concentrations in the sweat and the blood, opening up sweat as a medium for disease diagnosis and other general health monitoring applications. However, low concentration of analytes in sweat is a significant limitation, requiring high-performing sensors for this application. Electrochemical sensors, due to their high sensitivity, low cost, and miniaturization, play a crucial role in realizing the potential of sweat as a key sensing medium. MXenes, recently developed anisotropic two-dimensional atomic-layered nanomaterials composed of early transition metal carbides or nitrides, are currently being explored as a material of choice for electrochemical sensors. Their large surface area, tunable electrical properties, excellent mechanical strength, good dispersibility, and biocompatibility make them attractive for bio-electrochemical sensing platforms. This review presents the recent progress made in MXene-based bio-electrochemical sensors such as wearable, implantable, and microfluidic sensors and their applications in disease diagnosis and developing point-of-care sensing platforms. Finally, the paper discusses the challenges and limitations of MXenes as a material of choice in bio-electrochemical sensors and future perspectives on this exciting material for sweat-sensing applications.
Keywords: diagnostic; glucose monitoring; point-of-care; wearable sensor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Xiang L., Wang Y., Xia F., Liu F., He D., Long G., Zeng X., Liang X., Jin C., Wang Y., et al. An epidermal electronic system for physiological information acquisition, processing, and storage with an integrated flash memory array. Sci. Adv. 2023;8:eabp8075. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abp8075. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

