Various Applications of ZnO Thin Films Obtained by Chemical Routes in the Last Decade
- PMID: 37375229
- PMCID: PMC10304324
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28124674
Various Applications of ZnO Thin Films Obtained by Chemical Routes in the Last Decade
Abstract
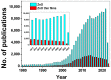
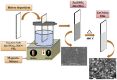
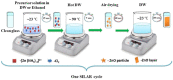
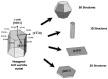
This review addresses the importance of Zn for obtaining multifunctional materials with interesting properties by following certain preparation strategies: choosing the appropriate synthesis route, doping and co-doping of ZnO films to achieve conductive oxide materials with p- or n-type conductivity, and finally adding polymers in the oxide systems for piezoelectricity enhancement. We mainly followed the results of studies of the last ten years through chemical routes, especially by sol-gel and hydrothermal synthesis. Zinc is an essential element that has a special importance for developing multifunctional materials with various applications. ZnO can be used for the deposition of thin films or for obtaining mixed layers by combining ZnO with other oxides (ZnO-SnO2, ZnO-CuO). Also, composite films can be achieved by mixing ZnO with polymers. It can be doped with metals (Li, Na, Mg, Al) or non-metals (B, N, P). Zn is easily incorporated in a matrix and therefore it can be used as a dopant for other oxidic materials, such as: ITO, CuO, BiFeO3, and NiO. ZnO can be very useful as a seed layer, for good adherence of the main layer to the substrate, generating nucleation sites for nanowires growth. Thanks to its interesting properties, ZnO is a material with multiple applications in various fields: sensing technology, piezoelectric devices, transparent conductive oxides, solar cells, and photoluminescence applications. Its versatility is the main message of this review.
Keywords: ZnO thin films; composite materials; doping; nanostructures; seed layer; sol-gel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Superior Conductivity of Transparent ZnO/MoS2 Composite Films for Optoelectronic and Solar Cell Applications.Gels. 2023 Nov 16;9(11):906. doi: 10.3390/gels9110906. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37998996 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication and characterization of a diluted magnetic semiconducting TM co-doped Al:ZnO (TM=Co, Ni) thin films by sol-gel spin coating method.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2013 Apr;106:118-23. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2013.01.017. Epub 2013 Jan 19. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2013. PMID: 23396005
-
Investigation of Photoluminescence and Optoelectronics Properties of Transition Metal-Doped ZnO Thin Films.Molecules. 2023 Dec 6;28(24):7963. doi: 10.3390/molecules28247963. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38138453 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Progress in Solution Processed Aluminum and co-Doped ZnO for Transparent Conductive Oxide Applications.Micromachines (Basel). 2023 Feb 25;14(3):536. doi: 10.3390/mi14030536. Micromachines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36984942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preparation and Application of Co-Doped Zinc Oxide: A Review.Molecules. 2024 Jul 18;29(14):3373. doi: 10.3390/molecules29143373. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39064951 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Optimization of short-circuit current density for tailored active region in BiFeO3 layer: a computational step into 3rd generation perovskite solar cells.RSC Adv. 2025 Jul 21;15(32):25799-25810. doi: 10.1039/d5ra03492b. eCollection 2025 Jul 21. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40697445 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sharma P., Hasan M.R., Mehto N.K., Deepak, Bishoyi A., Narang J. 92 years of zinc oxide: Has been studied by the scientific community since the 1930s- An overview. Sens. Int. 2022;3:100182. doi: 10.1016/j.sintl.2022.100182. - DOI
-
- Özgür Ü., Alivov Y.I., Liu C., Teke A., Reshchikov M.A., Doğan S., Avrutin V., Cho S.-J., Morkoç H. A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 2005;98:041301. doi: 10.1063/1.1992666. - DOI
-
- Ellmer K., Klein A. ZnO and Its Applications. In: Ellmer K., Klein A., Rech B., editors. Transparent Conductive Zinc Oxide: Basics and Applications in Thin Film Solar Cells. Springer; Berlin, Heidelberg: 2008. pp. 1–33.
-
- Borysiewicz M.A. ZnO as a Functional Material, a Review. Crystals. 2019;9:505. doi: 10.3390/cryst9100505. - DOI
-
- Nowak E., Szybowicz M., Stachowiak A., Koczorowski W., Schulz D., Paprocki K., Fabisiak K., Los S. A comprehensive study of structural and optical properties of ZnO bulk crystals and polycrystalline films grown by sol-gel method. Appl. Phys. A. 2020;126:552. doi: 10.1007/s00339-020-03711-2. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

