Mitigation of Hepatotoxicity via Boosting Antioxidants and Reducing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Carbendazim-Treated Rats Using Adiantum Capillus-Veneris L. Extract
- PMID: 37375275
- PMCID: PMC10300738
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28124720
Mitigation of Hepatotoxicity via Boosting Antioxidants and Reducing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Carbendazim-Treated Rats Using Adiantum Capillus-Veneris L. Extract
Abstract
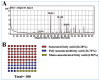
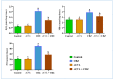
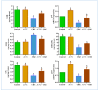
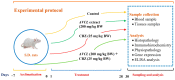
Exposure to food contaminants continues to be a substantial source of human health risks all over the world, particularly in developing countries. Carbendazim (CBZ) is a chemical fungicide used to control the spread of various fungi and other pathogens in the agriculture and veterinary sectors. The hazardous effects of CBZ on human health occur due to the accumulation of its residues in agricultural food products. In this study, the possible hepatoprotective effects of Adiantum capillus-veneris L. (ACVL) extract were evaluated in CBZ-treated rats. A GC-MS analysis revealed that ACVL extract contained several bioactive hydrocarbon components and fatty acids, and that the components exerted hepatic protection by mitigating oxidative stress via upregulating antioxidant agents and neutralizing nitrogen and oxygen free radicals. Moreover, ACVL extracts relieved hepatic inflammation via decreasing NO, NF-κB, and pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-a, IL-6) in the liver of CBZ-treated rats, both at protein and mRNA levels. In addition, the protective effect of ACVL has appeared in the histopathological figures and function markers in the livers of CBZ-treated rats. According to the present results, ACVL extract can protect the hepatic tissue and restore its functions to a control level in CBZ-treated rats; this effect may be attributed to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities.
Keywords: A. capillus-veneris L.; GC-MS; carbendazim; hepatotoxicity; protection; rats.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Adiantum capillus-veneris Linn protects female reproductive system against carbendazim toxicity in rats: immunohistochemical, histopathological, and pathophysiological studies.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021 Apr;28(16):19768-19782. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-11279-w. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33405113
-
Healing potential of Adiantum capillus-veneris L. plant extract on bisphenol A-induced hepatic toxicity in male albino rats.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 Apr;25(12):11884-11892. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-1211-3. Epub 2018 Feb 14. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29446025
-
Ethanol extract of Adiantum capillus-veneris L. suppresses the production of inflammatory mediators by inhibiting NF-κB activation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Jun 3;147(3):603-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.03.046. Epub 2013 Mar 27. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23542147
-
Bisphenol A exposure and healing effects of Adiantum capillus-veneris L. plant extract (APE) in bisphenol A-induced reproductive toxicity in albino rats.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016 Jun;23(12):11645-57. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6330-0. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016. PMID: 26936479
-
A Review of Pharmacological Properties and Toxicological Effects of Adiantum capillus-veneris L.Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2021;18(2):186-193. doi: 10.2174/1570163817666200316111445. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2021. PMID: 32178614 Review.
Cited by
-
Grape seed extract and L-ascorbic acid exert antineoplastic effects against solid Ehrlich carcinoma in vivo by modulating the tumor microenvironment and Th1/Th2 balance.Front Immunol. 2025 Aug 6;16:1635071. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1635071. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40843004 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Alzheimer's Potency of Rich Phenylethanoid Glycosides Extract from Marrubium vulgare L.: In Vitro and In Silico Studies.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Sep 27;17(10):1282. doi: 10.3390/ph17101282. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39458923 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the therapeutic potential of Saudi Kleinia anteuphorbium (L.) DC. Essential oil: Insights into antioxidant, analgesic, and hepatorenal protective effects.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 27;10(19):e38573. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38573. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39403475 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Russell P. The development of commercial disease control. Plant Pathol. 2006;55:585–594. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3059.2006.01440.x. - DOI
-
- Seif M., Deabes M., El-Askary A., El-Kott A.F., Albadrani G.M., Seif A., Wang Z. Ephedra sinica mitigates hepatic oxidative stress and inflammation via suppressing the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway in fipronil-treated rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021;28:62943–62958. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-15142-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Singh S., Singh N., Kumar V., Datta S., Wani A.B., Singh D., Singh K., Singh J. Toxicity, monitoring and biodegradation of the fungicide carbendazim. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2016;14:317–329. doi: 10.1007/s10311-016-0566-2. - DOI
-
- Chakraborty U., Kaur G., Chaudhary G.R. New Frontiers of Nanomaterials in Environmental Science. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2021. Development of Environmental Nanosensors for Detection Monitoring and Assessment; pp. 91–143.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

