Analysis of Network Pharmacological Efficacy and Therapeutic Effectiveness in Animal Models for Functional Dyspepsia of Foeniculi fructus
- PMID: 37375548
- PMCID: PMC10301275
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15122644
Analysis of Network Pharmacological Efficacy and Therapeutic Effectiveness in Animal Models for Functional Dyspepsia of Foeniculi fructus
Abstract
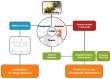
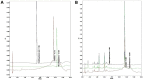
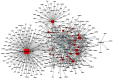
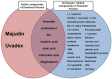
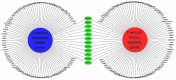
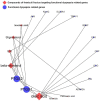
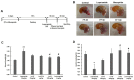
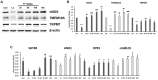
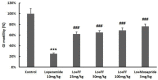
For centuries, Foeniculi fructus (F. fructus) has been used as a traditional herbal medicine in China and Europe and is widely used as a natural therapy for digestive disorders, including indigestion, flatulence, and bloating. The mechanism of F. fructus that alleviates functional dyspepsia was analyzed through network pharmacology, and its therapeutic effect on an animal model of functional dyspepsia were investigated. The traditional Chinese medicine systems pharmacology (TCMSP) database was used to investigate the compounds, targets, and associated diseases of F. fructus. Information on the target genes was classified using the UniProtdatabase. Using the Cytoscape 3.9.1 software, a network was constructed, and the Cytoscape string application was employed to examine genes associated with functional dyspepsia. The efficacy of F. fructus on functional dyspepsia was confirmed by treatment with its extract in a mouse model of loperamide-induced functional dyspepsia. Seven compounds targeted twelve functional dyspepsia-associated genes. When compared to the control group, F. fructus exhibited significant suppression of symptoms in a mouse model of functional dyspepsia. The results of our animal studies indicated a close association between the mechanism of action of F. fructus and gastrointestinal motility. Based on animal experimental results, the results showed that F. fructus provided a potential means to treat functional dyspepsia, suggesting that its medical mechanism for functional dyspepsia could be described by the relationship between seven key compounds of F. fructus, including oleic acid, β-sitosterol, and 12 functional dyspepsia-related genes.
Keywords: Foeniculi fructus; TCMSP; functional dyspepsia; network pharmacology; traditional medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

