Effect of Milk Protein and Whey Permeate in Large-Quantity Lipid-Based Nutrient Supplement on Early Child Development among Children with Stunting: A Randomized 2 × 2 Factorial Trial in Uganda
- PMID: 37375563
- PMCID: PMC10301406
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15122659
Effect of Milk Protein and Whey Permeate in Large-Quantity Lipid-Based Nutrient Supplement on Early Child Development among Children with Stunting: A Randomized 2 × 2 Factorial Trial in Uganda
Abstract
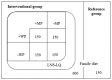
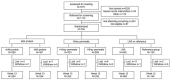
Stunting affects 22% children globally, putting them at risk of adverse outcomes including delayed development. We investigated the effect of milk protein (MP) vs. soy and whey permeate (WP) vs. maltodextrin in large-quantity, lipid-based nutrient supplement (LNS), and LNS itself vs. no supplementation, on child development and head circumference among stunted children aged 1-5 years. We conducted a randomized, double-blind, community-based 2 × 2 factorial trial in Uganda (ISRCTN1309319). We randomized 600 children to one of four LNS formulations (~535 kcal/d), with or without MP (n = 299 vs. n = 301) or WP (n = 301 vs. n = 299), for 12 weeks or to no supplementation (n = 150). Child development was assessed using the Malawi Development Assessment Tool. Data were analyzed using linear mixed-effects models. Children had a median [interquartile range] age of 30 [23; 41] months and mean ± standard deviation height-for-age z-score of -3.02 ± 0.74. There were no interactions between MP and WP for any of the outcomes. There was no effect of either MP or WP on any developmental domain. Although LNS itself had no impact on development, it resulted in 0.07 (95%CI: 0.004; 0.14) cm higher head circumference. Neither dairy in LNS, nor LNS in itself, had an effect on development among already stunted children.
Keywords: LNS; early child development; milk protein; stunting; whey permeate.
Conflict of interest statement
H.F. and C.M. have received research grants from ARLA Food for Health. H.F., B.G. and C.M. have received research grants from the Danish Dairy Research Foundation. C.M. and K.F.M. also received funds from Arla Foods Amba and finally H.F., C.M., K.F.M., B.G., S.F. and A.B. have had research collaboration with Nutriset, a producer of LNS. Other authors declare no financial relationships with any organisations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous five years, and declare no any other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) World Health Organization. International Bank for Reconstruction and Development/The World Bank . Levels and Trends in Child Malnutrition: Key Findings of the 2021 Edition of the Joint Child Malnutrition Estimates. United Nations Children’s Fund; New York, NY, USA: 2021.
-
- Dembélé B., Sanni M.A. Stunting and developmental delay in children in sub-Saharan Africa. Enfance. 2021;2:177–196. doi: 10.3917/enf2.212.0177. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

