Gut Microbiota Perturbation in Early Life Could Influence Pediatric Blood Pressure Regulation in a Sex-Dependent Manner in Juvenile Rats
- PMID: 37375565
- PMCID: PMC10304250
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15122661
Gut Microbiota Perturbation in Early Life Could Influence Pediatric Blood Pressure Regulation in a Sex-Dependent Manner in Juvenile Rats
Abstract
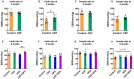
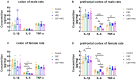
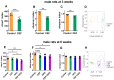
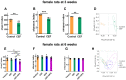
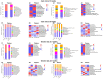
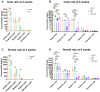
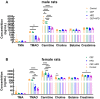
The present study aimed to investigate whether gut dysbiosis induced by ceftriaxone in early life could influence pediatric blood pressure regulation in childhood with or without exposure to a high-fat diet (HFD). Sixty-three newborn pups of Sprague-Dawley rats were administered ceftriaxone sodium or saline solution until weaning at 3 weeks, and the rats were fed a HFD or regular diet from 3 to 6 weeks. Tail-cuff blood pressure, the expression levels of genes of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS), the concentrations of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in the colon and prefrontal cortex, and the composition of fecal microbiota were analyzed. Ceftriaxone treatment significantly increased the diastolic blood pressure of male rats at 3 weeks. At 6 weeks, systolic blood pressure (SBP) was significantly increased only in ceftriaxone treated male rats fed with HFD. The RAS showed increased activation in the kidney, heart, hypothalamus, and thoracic and abdominal aorta of male rats, but only in the kidney, heart, and hypothalamus of female rats. HFD-fed female rats showed a decreased level of IL-6 in the colon. α diversity of gut microbiota decreased and the Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes ratio increased in both male and female rats at 3 weeks; however, these parameters recovered to various degrees in female rats at 6 weeks. These results revealed that early-life gut dysbiosis induced by antibiotics combined with a HFD in childhood could be involved in pediatric blood pressure regulation and an increase in SBP in juvenile rats, and these effects occurred in a sex-dependent manner.
Keywords: blood pressure; ceftriaxone; gut microbiota; high-fat diet; pediatric hypertension.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
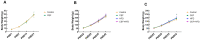
References
-
- Peng C., Li J., Miao Z., Wang Y., Wu S., Wang Y., Wang S., Cheng R., He F., Shen X. Early life administration of Bifidobacterium bifidum BD-1 alleviates long-term colitis by remodeling the gut microbiota and promoting intestinal barrier development. Front. Microbiol. 2022;13:916824. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.916824. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y., Liang H., Wang Y., Cheng R., Pu F., Yang Y., Li J., Wu S., Shen X., He F. Heat-inactivated Lacticaseibacillus paracasei N1115 alleviates the damage due to brain function caused by long-term antibiotic cocktail exposure in mice. BMC Neurosci. 2022;23:38. doi: 10.1186/s12868-022-00724-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

