Mast Cells as a Potential Target of Molecular Hydrogen in Regulating the Local Tissue Microenvironment
- PMID: 37375765
- PMCID: PMC10300919
- DOI: 10.3390/ph16060817
Mast Cells as a Potential Target of Molecular Hydrogen in Regulating the Local Tissue Microenvironment
Abstract
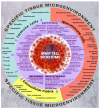
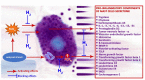
Knowledge of the biological effects of molecular hydrogen (H2), hydrogen gas, is constantly advancing, giving a reason for the optimism in several healthcare practitioners regarding the management of multiple diseases, including socially significant ones (malignant neoplasms, diabetes mellitus, viral hepatitis, mental and behavioral disorders). However, mechanisms underlying the biological effects of H2 are still being actively debated. In this review, we focus on mast cells as a potential target for H2 at the specific tissue microenvironment level. H2 regulates the processing of pro-inflammatory components of the mast cell secretome and their entry into the extracellular matrix; this can significantly affect the capacity of the integrated-buffer metabolism and the structure of the immune landscape of the local tissue microenvironment. The analysis performed highlights several potential mechanisms for developing the biological effects of H2 and offers great opportunities for translating the obtained findings into clinical practice.
Keywords: inflammation; local tissue microenvironment; mast cells; molecular hydrogen; reactive oxygen intermediates; secretome; specific mast cell proteases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- De Almeida A., de Oliveira J., da Silva Pontes L.V., de Souza Junior J.F., Goncalves T.A.F., Dantas S.H., de Almeida Feitosa M.S., Silva A.O., de Medeiros I.A. ROS: Basic Concepts, Sources, Cellular Signaling, and its Implications in Aging Pathways. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022;2022:1225578. doi: 10.1155/2022/1225578. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Villarreal-Garcia V., Estupinan-Jimenez J.R., Vivas-Mejia P.E., Gonzalez-Villasana V., Vazquez-Guillen J.M., Resendez-Perez D. A vicious circle in breast cancer: The interplay between inflammation, reactive oxygen species, and microRNAs. Front. Oncol. 2022;12:980694. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.980694. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

