Adenylosuccinic Acid: An Orphan Drug with Untapped Potential
- PMID: 37375769
- PMCID: PMC10304260
- DOI: 10.3390/ph16060822
Adenylosuccinic Acid: An Orphan Drug with Untapped Potential
Abstract
Adenylosuccinic acid (ASA) is an orphan drug that was once investigated for clinical application in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). Endogenous ASA participates in purine recycling and energy homeostasis but might also be crucial for averting inflammation and other forms of cellular stress during intense energy demand and maintaining tissue biomass and glucose disposal. This article documents the known biological functions of ASA and explores its potential application for the treatment of neuromuscular and other chronic diseases.
Keywords: ADSSL1 myopathy; Duchenne muscular dystrophy; Nrf2 activation; adenylosuccinate; adenylosuccinic acid; immunometabolism; metabolic disease; purine metabolism; skeletal muscle; succinyl-AMP.
Conflict of interest statement
E.R. has consulted for Santhera Pharmaceuticals and Epirium Bio previously. E.R.’s laboratory group is currently funded by the Estate of Charles A. Bonsett. AHB receives consulting income from Kate Therapeutics and Roche Pharmaceuticals, and has equity in Kate Therapeutics and Kinea Bio. The funders had no role in the design of the study, or in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data presented herein. The funders had no role in the writing of the manuscript, except for post-humous contributions made via previously unpublished FDA clinical trial reports (IND 17848).
Figures

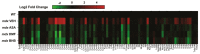

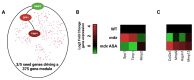
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

