Review on Additives in Hydrogels for 3D Bioprinting of Regenerative Medicine: From Mechanism to Methodology
- PMID: 37376148
- PMCID: PMC10302687
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15061700
Review on Additives in Hydrogels for 3D Bioprinting of Regenerative Medicine: From Mechanism to Methodology
Abstract
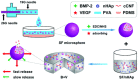
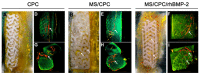
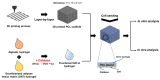
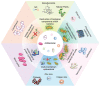
The regeneration of biological tissues in medicine is challenging, and 3D bioprinting offers an innovative way to create functional multicellular tissues. One common way in bioprinting is bioink, which is one type of the cell-loaded hydrogel. For clinical application, however, the bioprinting still suffers from satisfactory performance, e.g., in vascularization, effective antibacterial, immunomodulation, and regulation of collagen deposition. Many studies incorporated different bioactive materials into the 3D-printed scaffolds to optimize the bioprinting. Here, we reviewed a variety of additives added to the 3D bioprinting hydrogel. The underlying mechanisms and methodology for biological regeneration are important and will provide a useful basis for future research.
Keywords: 3D bioprinting; bioink; bionic scaffold; hydrogel; tissue engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

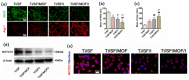
Similar articles
-
Advancing bioinks for 3D bioprinting using reactive fillers: A review.Acta Biomater. 2020 Sep 1;113:1-22. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.06.040. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 32622053 Review.
-
Hydrogels for 3D bioprinting in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: Current progress and challenges.Int J Bioprint. 2023 May 23;9(5):759. doi: 10.18063/ijb.759. eCollection 2023. Int J Bioprint. 2023. PMID: 37457925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3D Bioprinting of a Bioactive Composite Scaffold for Cell Delivery in Periodontal Tissue Regeneration.Biomolecules. 2023 Jun 30;13(7):1062. doi: 10.3390/biom13071062. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37509098 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Decellularized Matrix-Derived Materials for Bioink and 3D Bioprinting.Gels. 2023 Mar 3;9(3):195. doi: 10.3390/gels9030195. Gels. 2023. PMID: 36975644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioprinting of alginate-carboxymethyl chitosan scaffolds for enamel tissue engineeringin vitro.Biofabrication. 2022 Dec 30;15(1). doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/acab35. Biofabrication. 2022. PMID: 36583240
Cited by
-
Injectable Decellularized Extracellular Matrix-Based Bio-Ink with Excellent Biocompatibility for Scarless Urethra Repair.Gels. 2023 Nov 17;9(11):913. doi: 10.3390/gels9110913. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37999003 Free PMC article.
-
Scaffold-Based (Matrigel™) 3D Culture Technique of Glioblastoma Recovers a Patient-like Immunosuppressive Phenotype.Cells. 2023 Jul 14;12(14):1856. doi: 10.3390/cells12141856. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37508520 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of the Methacrylation Process on the Usefulness of Chitosan as a Biomaterial Component for 3D Printing.J Funct Biomater. 2024 Aug 30;15(9):251. doi: 10.3390/jfb15090251. J Funct Biomater. 2024. PMID: 39330227 Free PMC article.
-
Light-based 3D bioprinting technology applied to repair and regeneration of different tissues: A rational proposal for biomedical applications.Mater Today Bio. 2024 Jun 26;27:101135. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101135. eCollection 2024 Aug. Mater Today Bio. 2024. PMID: 39040222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sustainable Hydrogels for Medical Applications: Biotechnological Innovations Supporting One Health.Gels. 2025 Jul 21;11(7):559. doi: 10.3390/gels11070559. Gels. 2025. PMID: 40710720 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beheshtizadeh N., Lotfibakhshaiesh N., Pazhouhnia Z., Hoseinpour M., Nafari M. A review of 3D bio-printing for bone and skin tissue engineering: A commercial approach. J. Mater. Sci. 2020;55:3729–3749. doi: 10.1007/s10853-019-04259-0. - DOI
-
- Hassan M., Dave K., Chandrawati R., Dehghani F., Gomes V.G. 3D printing of biopolymer nanocomposites for tissue engineering: Nanomaterials, processing and structure-function relation. Eur. Polym. J. 2019;121:109340. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2019.109340. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

