Review on Additives in Hydrogels for 3D Bioprinting of Regenerative Medicine: From Mechanism to Methodology
- PMID: 37376148
- PMCID: PMC10302687
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15061700
Review on Additives in Hydrogels for 3D Bioprinting of Regenerative Medicine: From Mechanism to Methodology
Abstract
The regeneration of biological tissues in medicine is challenging, and 3D bioprinting offers an innovative way to create functional multicellular tissues. One common way in bioprinting is bioink, which is one type of the cell-loaded hydrogel. For clinical application, however, the bioprinting still suffers from satisfactory performance, e.g., in vascularization, effective antibacterial, immunomodulation, and regulation of collagen deposition. Many studies incorporated different bioactive materials into the 3D-printed scaffolds to optimize the bioprinting. Here, we reviewed a variety of additives added to the 3D bioprinting hydrogel. The underlying mechanisms and methodology for biological regeneration are important and will provide a useful basis for future research.
Keywords: 3D bioprinting; bioink; bionic scaffold; hydrogel; tissue engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
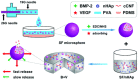
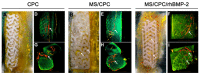
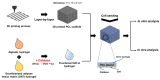
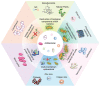
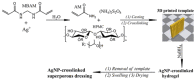
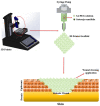

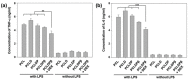
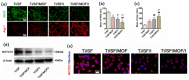
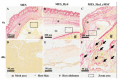
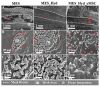
References
-
- Beheshtizadeh N., Lotfibakhshaiesh N., Pazhouhnia Z., Hoseinpour M., Nafari M. A review of 3D bio-printing for bone and skin tissue engineering: A commercial approach. J. Mater. Sci. 2020;55:3729–3749. doi: 10.1007/s10853-019-04259-0. - DOI
-
- Hassan M., Dave K., Chandrawati R., Dehghani F., Gomes V.G. 3D printing of biopolymer nanocomposites for tissue engineering: Nanomaterials, processing and structure-function relation. Eur. Polym. J. 2019;121:109340. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2019.109340. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

