New Ruthenium-Cyclopentadienyl Complexes Affect Colorectal Cancer Hallmarks Showing High Therapeutic Potential
- PMID: 37376178
- PMCID: PMC10302444
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15061731
New Ruthenium-Cyclopentadienyl Complexes Affect Colorectal Cancer Hallmarks Showing High Therapeutic Potential
Abstract
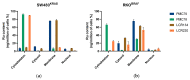
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is among the most deadly cancers worldwide. Current therapeutic strategies have low success rates and several side effects. This relevant clinical problem requires the discovery of new and more effective therapeutic alternatives. Ruthenium drugs have arisen as one of the most promising metallodrugs, due to their high selectivity to cancer cells. In this work we studied, for the first time, the anticancer properties and mechanisms of action of four lead Ru-cyclopentadienyl compounds, namely PMC79, PMC78, LCR134 and LCR220, in two CRC-derived cell lines (SW480 and RKO). Biological assays were performed on these CRC cell lines to evaluate cellular distribution, colony formation, cell cycle, proliferation, apoptosis, and motility, as well as cytoskeleton and mitochondrial alterations. Our results show that all the compounds displayed high bioactivity and selectivity, as shown by low half-maximal inhibitory concentrations (IC50) against CRC cells. We observed that all the Ru compounds have different intracellular distributions. In addition, they inhibit to a high extent the proliferation of CRC cells by decreasing clonogenic ability and inducing cell cycle arrest. PMC79, LCR134, and LCR220 also induce apoptosis, increase the levels of reactive oxygen species, lead to mitochondrial dysfunction, induce actin cytoskeleton alterations, and inhibit cellular motility. A proteomic study revealed that these compounds cause modifications in several cellular proteins associated with the phenotypic alterations observed. Overall, we demonstrate that Ru compounds, especially PMC79 and LCR220, display promising anticancer activity in CRC cells with a high potential to be used as new metallodrugs for CRC therapy.
Keywords: active targeting; colorectal cancer; passive targeting; ruthenium-cyclopentadienyl compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

























Similar articles
-
Ruthenium(II)-Cyclopentadienyl-Derived Complexes as New Emerging Anti-Colorectal Cancer Drugs.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jun 17;14(6):1293. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14061293. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35745864 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer Activity and In Vitro to In Vivo Mechanistic Recapitulation of Novel Ruthenium-Based Metallodrugs in the Zebrafish Model.Toxicol Sci. 2021 Jul 16;182(1):29-43. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfab041. Toxicol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33822233 Free PMC article.
-
Polymer "ruthenium-cyclopentadienyl" conjugates - New emerging anti-cancer drugs.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 Apr 15;168:373-384. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.02.061. Epub 2019 Feb 25. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30826512
-
Ruthenium Complexes: An Alternative to Platinum Drugs in Colorectal Cancer Treatment.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Aug 19;13(8):1295. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13081295. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34452256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vanadium, Ruthenium and Copper Compounds: A New Class of Nonplatinum Metallodrugs with Anticancer Activity.Curr Med Chem. 2017;24(2):112-148. doi: 10.2174/0929867323666160824162546. Curr Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27554807 Review.
Cited by
-
Colorectal cancer: Recent advances in management and treatment.World J Clin Oncol. 2024 Sep 24;15(9):1136-1156. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i9.1136. World J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39351451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cutting-Edge Advances in Anticancer Therapies: Insights from the Third Edition of the Special Issue "Novel Anticancer Strategies".Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jan 3;17(1):54. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17010054. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 39861702 Free PMC article.
-
Fighting Multidrug Resistance with Ruthenium-Cyclopentadienyl Compounds: Unveiling the Mechanism of P-gp Inhibition.J Med Chem. 2023 Oct 26;66(20):14080-14094. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c01120. Epub 2023 Aug 24. J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37616241 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Van Cutsem E., Cervantes A., Adam R., Sobrero A., van Krieken J.H., Aderka D., Aguilar E.A., Bardelli A., Benson A., Bodoky G., et al. ESMO consensus guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2016;27:1386–1422. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw235. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cazzanelli G., Moreira T., Ferro S., Azevedo-Silva J., Nogueira E., Preto A. Frontiers in Anti-Cancer Drug Discovery. Bentham Books; Sharjah, UAE: 2016. Colorectal Cancer Therapeutic Approaches: From Classical Drugs to New Nanoparticles.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

