Effectiveness of exercise intervention on improving fundamental motor skills in children with autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37377477
- PMCID: PMC10291092
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1132074
Effectiveness of exercise intervention on improving fundamental motor skills in children with autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a severe public health concern, and most of the children with ASD experience a substantial delay in FMS. This study aimed to investigate the effectiveness of exercise interventions in improving FMS in children with ASD, and provide evidence to support the scientific use of exercise interventions in practice.
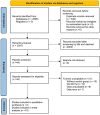
Methods: We searched seven online databases (PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, Embase, EBSCO, Clinical Trials, and The Cochrane Library) from inception to May 20, 2022. We included randomized control trials of exercise interventions for FMS in children with ASD. The methodological quality of the included studies was assessed using the Physiotherapy Evidence Database Scale. Stata 14.0 software was used for meta-analysis, forest plotting, subgroup analysis, heterogeneity analysis, and meta-regression.
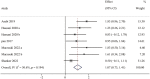
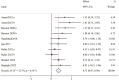
Results: Thirteen studies underwent systematic review (541 participants), of which 10 underwent meta-analysis (297 participants). Overall, exercise interventions significantly improved overall FMS in children with ASD. Regarding the three categories of FMS, exercise interventions significantly improved LMS (SMD = 1.07; 95% CI 0.73 to 1.41, p < 0.001), OCS (SMD = 0.79; 95% CI 0.32 to 1.26, p = 0.001), and SS (SMD = 0.72; 95% CI 0.45 to 0.98, p < 0.0001).
Conclusion: exercise interventions can effectively improve the FMS of children with ASD. The effects on LMS are considered as large effect sizes, while the effects on OCS and SS are considered as moderate effect sizes. These findings can inform clinical practice.
Systematic review registration: https://inplasy.com/inplasy-2022-12-0013/.
Keywords: autism spectrum disorder; children; exercise; fundamental motor skills; meta-analysis.
Copyright © 2023 Ji, Tian, Zheng, Ye and Ye.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association A, Association AP. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: Dsm-5: Washington, DC: American psychiatric association; (2013). 10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596 - DOI
-
- Calhoun SL, Pearl AM, Fernandez-Mendoza J, Durica KC, Mayes SD, Murray MJ. Sleep disturbances increase the impact of working memory deficits on learning problems in adolescents with high-functioning autism spectrum disorder. J Autism Dev Disord. (2020) 50:1701–13. 10.1007/s10803-019-03928-y - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous