Reprogramming of Tumor-reactive Tumor-infiltrating Lymphocytes to Human-induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
- PMID: 37377887
- PMCID: PMC10211394
- DOI: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-22-0265
Reprogramming of Tumor-reactive Tumor-infiltrating Lymphocytes to Human-induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Abstract
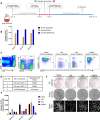
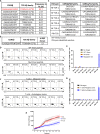
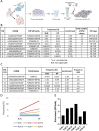
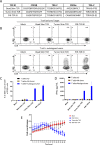
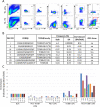
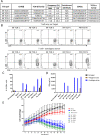
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) that can recognize and kill tumor cells have curative potential in subsets of patients treated with adoptive cell transfer (ACT). However, lack of TIL therapeutic efficacy in many patients may be due in large part to a paucity of tumor-reactive T cells in TIL and the exhausted and terminally differentiated status of those tumor-reactive T cells. We sought to reprogram exhausted TIL that possess T-cell receptors (TCR) specific for tumor antigens into induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC) to rejuvenate them for more potent ACT. We first attempted to reprogram tumor neoantigen-specific TIL by αCD3 Ab prestimulation which resulted in failure of establishing tumor-reactive TIL-iPSCs, instead, T cell-derived iPSCs from bystander T cells were established. To selectively activate and enrich tumor-reactive T cells from the heterogenous TIL population, CD8+ PD-1+ 4-1BB+ TIL population were isolated after coculture with autologous tumor cells, followed by direct reprogramming into iPSCs. TCR sequencing analysis of the resulting iPSC clones revealed that reprogrammed TIL-iPSCs encoded TCRs that were identical to the pre-identified tumor-reactive TCRs found in minimally cultured TIL. Moreover, reprogrammed TIL-iPSCs contained rare tumor antigen-specific TCRs, which were not detectable by TCR sequencing of the starting cell population. Thus, reprogramming of PD-1+ 4-1BB+ TIL after coculture with autologous tumor cells selectively generates tumor antigen-specific TIL-iPSCs, and is a distinctive method to enrich and identify tumor antigen-specific TCRs of low frequency from TIL.
Significance: Reprogramming of TIL into iPSC holds great promise for the future treatment of cancer due to their rejuvenated nature and the retention of tumor-specific TCRs. One limitation is the lack of selective and efficient methods for reprogramming tumor-specific T cells from polyclonal TIL. Here we addressed this limitation and present a method to efficiently reprogram TIL into iPSC colonies carrying diverse tumor antigen reactive TCR recombination.
© 2023 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
References
-
- Besser MJ, Shapira-Frommer R, Itzhaki O, Treves AJ, Zippel DB, Levy D, et al. . Adoptive transfer of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients with metastatic melanoma: intent-to-treat analysis and efficacy after failure to prior immunotherapies. Clin Cancer Res 2013;19:4792–800. - PubMed
-
- Andersen R, Donia M, Ellebaek E, Borch TH, Kongsted P, Iversen TZ, et al. . Long-lasting complete responses in patients with metastatic melanoma after adoptive cell therapy with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and an attenuated IL2 regimen. Clin Cancer Res 2016;22:3734–45. - PubMed
-
- Sarnaik A, Khushalani NI, Chesney JA, Kluger HM, Curti BD, Lewis KD, et al. . Safety and efficacy of cryopreserved autologous tumor infiltrating lymphocyte therapy (LN-144, lifileucel) in advanced metastatic melanoma patients who progressed on multiple prior therapies including anti-PD-1. J Clin Oncol 37: 15s, 2019. (suppl; abstr 2518).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

