Hypoxia-altered cholesterol homeostasis enhances the expression of interferon-stimulated genes upon SARS-CoV-2 infections in monocytes
- PMID: 37377965
- PMCID: PMC10291055
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1121864
Hypoxia-altered cholesterol homeostasis enhances the expression of interferon-stimulated genes upon SARS-CoV-2 infections in monocytes
Abstract
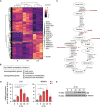
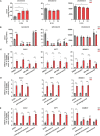
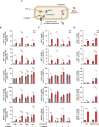
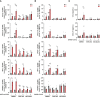
Hypoxia contributes to numerous pathophysiological conditions including inflammation-associated diseases. We characterized the impact of hypoxia on the immunometabolic cross-talk between cholesterol and interferon (IFN) responses. Specifically, hypoxia reduced cholesterol biosynthesis flux and provoked a compensatory activation of sterol regulatory element-binding protein 2 (SREBP2) in monocytes. Concomitantly, a broad range of interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) increased under hypoxia in the absence of an inflammatory stimulus. While changes in cholesterol biosynthesis intermediates and SREBP2 activity did not contribute to hypoxic ISG induction, intracellular cholesterol distribution appeared critical to enhance hypoxic expression of chemokine ISGs. Importantly, hypoxia further boosted chemokine ISG expression in monocytes upon infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus type 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Mechanistically, hypoxia sensitized toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling to activation by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, which emerged as a major signaling hub to enhance chemokine ISG induction following SARS-CoV-2 infection of hypoxic monocytes. These data depict a hypoxia-regulated immunometabolic mechanism with implications for the development of systemic inflammatory responses in severe cases of coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19).
Keywords: COVID-19; SREBP2; cholesterol; hypoxia; immunometabolism; systemic inflammation.
Copyright © 2023 Bauer, Meyer, Raue, Palmer, Guerrero Ruiz, Cardamone, Rösser, Heffels, Roesmann, Wilhelm, Lütjohann, Zarnack, Fuhrmann, Widera, Schmid and Brüne.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

