High-resolution shape models of Phobos and Deimos from stereophotoclinometry
- PMID: 37378051
- PMCID: PMC10290967
- DOI: 10.1186/s40623-023-01814-7
High-resolution shape models of Phobos and Deimos from stereophotoclinometry
Abstract
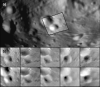
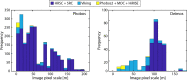
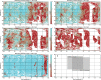
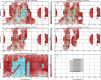
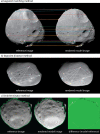
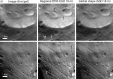
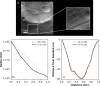
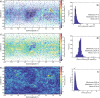
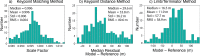
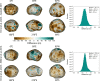
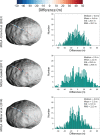
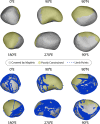
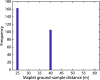
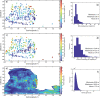
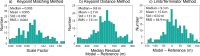
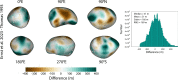
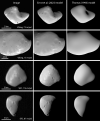
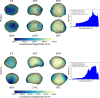
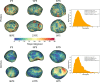
We created high-resolution shape models of Phobos and Deimos using stereophotoclinometry and united images from Viking Orbiter, Phobos 2, Mars Global Surveyor, Mars Express, and Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter into a single coregistered collection. The best-fit ellipsoid to the Phobos model has radii of (12.95 ± 0.04) km × (11.30 ± 0.04) km × (9.16 ± 0.03) km, with an average radius of (11.08 ± 0.04) km. The best-fit ellipsoid to the Deimos model has radii of (8.04 ± 0.08) km × (5.89 ± 0.06) km × (5.11 ± 0.05) km with an average radius of (6.27 ± 0.07) km. The new shape models offer substantial improvements in resolution over existing shape models, while remaining globally consistent with them. The Phobos model resolves grooves, craters, and other surface features ~ 100 m in size across the entire surface. The Deimos model is the first to resolve geological surface features. These models, associated data products, and a searchable, coregistered collection of images across six spacecraft are publicly available in the Small Body Mapping Tool, and will be archived with the NASA Planetary Data System. These products enable an array of future studies to advance the understanding of Phobos and Deimos, facilitate coregistration of other past and future datasets, and set the stage for planning and operating future missions to the moons, including the upcoming Martian Moons eXploration (MMX) mission.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s40623-023-01814-7.
Keywords: Deimos; Martian Moons eXploration; Martian moons; Phobos; Shape; Small bodies; Stereophotoclinometry; Topography.
© The Author(s) 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Archinal BA, A’Hearn MF, Bowell E, et al. Report of the IAU working group on cartographic coordinates and rotational elements: 2009. Celest Mech Dyn Astron. 2011;109:101–135. doi: 10.1007/s10569-010-9320-4. - DOI
-
- Archinal BA, Acton C, A’Hearn MF, et al. Report of the IAU working group on cartographic coordinates and rotational elements: 2015. Celest Mech Dyn Astron. 2018;130:22. doi: 10.1007/s10569-017-9805-5. - DOI
-
- Archinal BA, Acton C, Conrad A, et al. Erratum: correction to: report of the IAU working group on cartographic coordinates and rotational elements: 2015. Celest Mech Dyn Astron. 2019;131:61. doi: 10.1007/s10569-019-9925-1. - DOI
-
- Al Asad MM, Philpott LC, Johnson CL, et al. Validation of Stereophotoclinometric shape models of asteroid (101955) Bennu during the OSIRIS-REx Mission. Planet Sci J. 2021;2:82. doi: 10.3847/PSJ/abe4dc. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
