Diagnosis and Treatment of Cardiac Myxoma
- PMID: 37378149
- PMCID: PMC10292048
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.39148
Diagnosis and Treatment of Cardiac Myxoma
Abstract
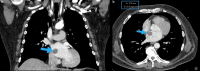
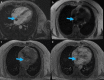
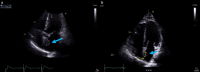
Cardiac myxoma is the most common primary cardiac neoplasm. It is a benign tumor that typically arises in the left atrium, specifically from the interatrial septum adjacent to the fossa ovalis. We present a case of a 71-year-old male presenting with hematuria that was incidentally found to have a left atrial myxoma on a CT urogram. Follow-up CT and MRI of the heart demonstrated findings compatible with myxoma. Cardiothoracic surgery was consulted, and the patient underwent resection of the left atrial mass, which was confirmed to be a myxoma on pathology.
Keywords: cardiac myxoma; cardiac neoplasm; cardiac tumor; cardiology cardiac ct and mri; mri cardiac.
Copyright © 2023, Manche et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Long-term follow-up of 82 patients after surgical excision of atrial myxomas. Vroomen M, Houthuizen P, Khamooshian A, Soliman Hamad MA, van Straten AH. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2015;21:183–188. - PubMed
-
- MR imaging of cardiac tumors. Sparrow PJ, Kurian JB, Jones TR, Sivananthan MU. Radiographics. 2005;25:1255–1276. - PubMed
-
- Cardiac myxoma: imaging features in 83 patients. Grebenc ML, Rosado-de-Christenson ML, Green CE, Burke AP, Galvin JR. Radiographics. 2002;22:673–689. - PubMed
-
- Atrial myxomas grow faster than we think. Walpot J, Shivalkar B, Rodrigus I, Pasteuning WH, Hokken R. Echocardiography. 2010;27:0–31. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
