AXL Inhibition Improves the Antitumor Activity of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells
- PMID: 37378662
- PMCID: PMC10530462
- DOI: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-22-0254
AXL Inhibition Improves the Antitumor Activity of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells
Abstract
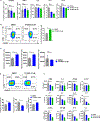
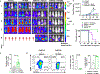
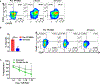
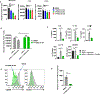
The receptor tyrosine kinase AXL is a member of the TYRO3, AXL, and proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase MER family and plays pleiotropic roles in cancer progression. AXL is expressed in immunosuppressive cells, which contributes to decreased efficacy of immunotherapy. Therefore, we hypothesized that AXL inhibition could serve as a strategy to overcome resistance to chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR T)-cell therapy. To test this, we determined the impact of AXL inhibition on CD19-targeted CAR T (CART19)-cell functions. Our results demonstrate that T cells and CAR T cells express high levels of AXL. Specifically, higher levels of AXL on activated Th2 CAR T cells and M2-polarized macrophages were observed. AXL inhibition with small molecules or via genetic disruption in T cells demonstrated selective inhibition of Th2 CAR T cells, reduction of Th2 cytokines, reversal of CAR T-cell inhibition, and promotion of CAR T-cell effector functions. AXL inhibition is a novel strategy to enhance CAR T-cell functions through two independent, but complementary, mechanisms: targeting Th2 cells and reversing myeloid-induced CAR T-cell inhibition through selective targeting of M2-polarized macrophages.
©2023 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
SSK is an inventor on patents in the field of CAR immunotherapy that are licensed to Novartis (through an agreement between Mayo Clinic, University of Pennsylvania, and Novartis). RLS, MJC, and SSK are inventors on patents in the field of CAR immunotherapy that are licensed to Humanigen (through Mayo Clinic). SSK and MH are inventors on patents in the field of CAR immunotherapy that are licensed to Mettaforge (through Mayo Clinic). SSK and IC are inventors on patients that are licensed to Sendero (through Mayo Clinic). SSK is an inventor on intellectual property that is licensed to MustangBio (through Mayo Clinic). SSK receives research funding from Kite, Gilead, Juno, Celgene, Novartis, Humanigen, MorphoSys, Tolero, Sunesis, LeahLabs, and Lentigen. SSK has participated in advisory meetings of Juno, Celgene, Kite, Gilead, LeahLabs, CapstanBio, Torque, Luminary, and Humanigen. SSK has participated in data safety monitoring boards of Humanigen. RLS, LM, JF, SLW, NEK, and SSK are inventors on patents related to this work. NEK receives research funding from Acerta Pharma, BMS, Pharmacyclics, MEI Pharma, and Sunesis. NEK has participated in Advisory Board meetings of Cytomx Therapy, Janssen, Juno Therapeutics, Astra Zeneca, and Oncotracker; and on DSMC for Agios and Cytomx Therapeutics. SAP receives research funding from Pharmacyclics, MorphoSys, Janssen, AstraZeneca, TG Therapeutics, Bristol Myers Squibb, AbbVie, and Ascentage Pharma. SAP has participated in Advisory Board meetings of Pharmacyclics, AstraZeneca, Genentech, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Verastem Oncology, and AbbVie (he was not personally compensated for his participation).
Figures

References
-
- van der Meer JHM, van der Poll T, van ‘t Veer C. TAM receptors, Gas6, and protein S: roles in inflammation and hemostasis. Blood 2014;123:2460–9 - PubMed
-
- Vouri M, Hafizi S. TAM Receptor Tyrosine Kinases in Cancer Drug Resistance. Cancer Res 2017;77:2775–8 - PubMed
-
- Seitz HM, Camenisch TD, Lemke G, Earp HS, Matsushima GK. Macrophages and dendritic cells use different AXL/Mertk/Tyro3 receptors in clearance of apoptotic cells. J Immunol 2007;178:5635–42 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

