Efficacy and Safety of IL-12/23 and IL-23 Inhibitors for Crohn's Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 37378711
- PMCID: PMC10981469
- DOI: 10.1007/s10620-023-08014-z
Efficacy and Safety of IL-12/23 and IL-23 Inhibitors for Crohn's Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Targeting interleukin-23 (IL-23) is an important therapeutic strategy for Crohn's disease (CD).
Aims: This systematic review and meta-analysis assessed the efficacy and safety of selective IL-23p19 and IL-12/23p40 inhibitors in patients with moderate-to-severe CD.
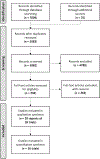
Methods: MEDLINE, Embase, and the Cochrane library (CENTRAL) were searched from inception to May 24, 2023, for randomized, placebo- or active comparator-controlled induction and/or maintenance trials of selective IL-23p19 and IL-12/23p40 inhibitors in pediatric and adult patients with CD. The primary outcome was the proportion of patients in clinical remission. Secondary outcomes were clinical response, endoscopic remission, endoscopic response, and safety. Data were pooled using a random-effects model. Risk of bias and certainty of evidence were assessed using the Cochrane risk of bias tool and the GRADE criteria, respectively.
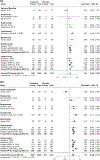
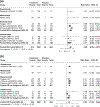
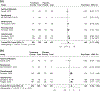
Results: Eighteen trials (n = 5561) were included. Most studies were rated as low risk of bias. Targeting IL-23 was significantly superior to placebo for inducing clinical (risk ratio [RR] = 1.87, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.58-2.21) and endoscopic (RR = 3.20, 95%CI 2.17-4.70) remission and maintaining clinical remission (RR = 1.39, 95%CI 1.10-1.77) (GRADE high certainty evidence for all outcomes). Subgroup analysis showed that targeting IL-23 was superior to placebo for inducing clinical remission in biologic-naïve (RR = 2.20, 95%CI 1.46-3.32, I2 = 0%, p = 0.39) and biologic-experienced patients (RR = 1.82, 95%CI 1.27-2.60, I2 = 56.5%, p = 0.01). Targeting IL-23 was associated with a decreased risk of serious adverse events in induction (RR = 0.55, 95%CI 0.44-0.73) and maintenance (RR = 0.72, 95%CI 0.53-0.98) trials compared to placebo (high certainty evidence).
Conclusion: Targeting IL-23 is effective and safe for inducing and maintaining clinical and endoscopic remission in patients with moderate-to-severe CD.
Keywords: Biologic therapy; Crohn’s disease; Inflammatory bowel disease; Interleukin-23 inhibitors; Risankizumab; Ustekinumab.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations
Figures
References
-
- Hanauer SB, Feagan BG, Lichtenstein GR et al. Maintenance infliximab for Crohn’s disease: the ACCENT I randomised trial. Lancet. 2002;359:1541–1549. - PubMed
-
- Gisbert JP, Marín AC, McNicholl AG, Chaparro M. Systematic review with meta-analysis: the efficacy of a second anti-TNF in patients with inflammatory bowel disease whose previous anti-TNF treatment has failed. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015;41:613–623. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

