Decreasing incidence of conjunctival squamous cell carcinoma in people with HIV in South Africa
- PMID: 37379162
- PMCID: PMC10560597
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djad119
Decreasing incidence of conjunctival squamous cell carcinoma in people with HIV in South Africa
Abstract
Background: The main risk factors for squamous cell carcinoma of the conjunctiva (SCCC) are immunodeficiency and exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Little is known about SCCC epidemiology among people with HIV (PWH) in South Africa.
Methods: We used data from the South African HIV Cancer Match study, a nation-wide cohort of PWH in South Africa, created through a privacy-preserving probabilistic record linkage of HIV-related laboratory records from the National Health Laboratory Service and cancer records from the National Cancer Registry from 2004 to 2014. We calculated crude incidence rates, analyzed trends using joinpoint models, and estimated hazard ratios for different risk factors using Royston-Parmar flexible parametric survival models.
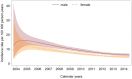
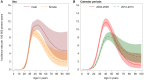
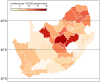
Results: Among 5 247 968 PWH, 1059 cases of incident SCCC were diagnosed, for a crude overall SCCC incidence rate of 6.8 per 100 000 person-years. The SCCC incidence rate decreased between 2004 and 2014, with an annual percentage change of ‒10.9% (95% confidence interval: ‒13.3 to ‒8.3). PWH residing within latitudes 30°S to 34°S had a 49% lower SCCC risk than those residing at less than 25°S latitude (adjusted hazard ratio = 0.67; 95% confidence interval: 0.55 to 0.82). Other risk factors for SCCC were lower CD4 counts and middle age. There was no evidence for an association of sex or settlement type with SCCC risk.
Conclusions: An increased risk of developing SCCC was associated with lower CD4 counts and residence closer to the equator, indicative of higher ultraviolet radiation exposure. Clinicians and PWH should be educated on known SCCC preventive measures, such as maintaining high CD4 counts and protection from ultraviolet radiation through sunglasses and sunhats when outdoors.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state that they have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Comment in
-
Conjunctival squamous cell carcinoma in people with HIV in South Africa: time to renew efforts for novel oncogenic virus discovery?J Natl Cancer Inst. 2024 Feb 8;116(2):186-188. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djad147. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2024. PMID: 37603725 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Biological agents. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum. 2012;100(Pt B):1-441. https://publications.iarc.fr/119. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

