Measuring effects of screen time on the development of children in the Philippines: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 37380949
- PMCID: PMC10308687
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-023-16188-4
Measuring effects of screen time on the development of children in the Philippines: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Screen time in young children is discouraged because of its negative effects on their development. However, excessive screen media use has been rising, particularly during the global pandemic when stay-at-home mandates were placed on young children in several countries. This study documents potential developmental effects of excessive screen media use.
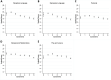
Method: This is a cross-sectional study. Participants were 24 to 36 month old Filipino children recruited through non-probable convenience sampling from August to October 2021. Regression analyses were performed to test the association between screen time and changes in scaled scores for skills and behaviors determined from the Adaptive Behavior Scale and to identify factors associated with increased screen media use.
Results: Increased odds of excessive use of screen media of children by 4.19 when parents watch excessively and 8.56 times greater odds when children are alone compared to watching with a parent or other children. When adjusted for co-viewing, more than 2 h of screen time is significantly associated with decrease in receptive and expressive language scores. The effects on personal skills, interpersonal relationships and play and leisure skills were only statistically significant at 4 to 5 or more hours of screen time use.
Conclusion: The study found that spending no more than 2 h screen time had minimal negative effects on development and that use beyond 2 h was associated with poorer language development among 2 year olds. There is less excessive screen media use when a child co-views with an adult, sibling or other child and when parents likewise have less screen time themselves.
Keywords: Child development; Language development; Parenting; Screen time.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Excessive Screen Media Use in Preschoolers Is Associated with Poor Motor Skills.Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. 2020 Jun;23(6):418-425. doi: 10.1089/cyber.2019.0238. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. 2020. PMID: 32511011
-
Associations Between Screen-Based Media Use and Brain White Matter Integrity in Preschool-Aged Children.JAMA Pediatr. 2020 Jan 1;174(1):e193869. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.3869. Epub 2020 Jan 6. JAMA Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 31682712 Free PMC article.
-
Screen time of children with speech delay: a cross-sectional study in a tertiary center in Kuantan, Malaysia.Pediatr Int. 2022 Jan;64(1):e15105. doi: 10.1111/ped.15105. Pediatr Int. 2022. PMID: 35411977
-
Associations Between Screen Use and Child Language Skills: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Pediatr. 2020 Jul 1;174(7):665-675. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.0327. JAMA Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32202633 Free PMC article.
-
[Screen viewing in children under 3 years old: a review of correlates based on socio-ecological models].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2023 Sep 2;61(9):852-855. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112140-20230608-00387. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37650171 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Screen Time and Its Health Consequences in Children and Adolescents.Children (Basel). 2023 Oct 8;10(10):1665. doi: 10.3390/children10101665. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37892328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Screen Time Matters: Exploring the Behavioral Effects of Devices on Saudi Children.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025 May 8;22(5):741. doi: 10.3390/ijerph22050741. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40427857 Free PMC article.
-
Association of digital media use with sleep habits in school children: A cross-sectional study.Sleep Med X. 2024 Jun 12;8:100117. doi: 10.1016/j.sleepx.2024.100117. eCollection 2024 Dec 15. Sleep Med X. 2024. PMID: 38994446 Free PMC article.
-
The longitudinal impact of screen media activities on brain function, architecture and mental health in early adolescence.Int J Clin Health Psychol. 2025 Jul-Sep;25(3):100589. doi: 10.1016/j.ijchp.2025.100589. Epub 2025 Jun 14. Int J Clin Health Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40584278 Free PMC article.
-
Digital Intervention in Children With Developmental Language Disorder: Systematic Review.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2025 May 23;13:e59992. doi: 10.2196/59992. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2025. PMID: 40407714 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kemp S. Digital 2023: Global overview report [Internet]. Datareportal; 2023 Jan [cited 2023 Apr 8]. Available from: https://datareportal.com/reports/digital-2023-global-overview-report.
-
- Kemp S. Digital in the Philippines: All the Statistics You Need in 2021 — DataReportal – Global Digital Insights [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2021 Jun 4]. Available from: https://datareportal.com/reports/digital-2021-philippines.
-
- GWI. 2020 Consumer Trends in Digital Device Usage - GlobalWebIndex [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2021 Jun 4]. Available from: https://www.gwi.com/reports/device.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

