Anti-amyloid therapies for Alzheimer disease: finally, good news for patients
- PMID: 37381015
- PMCID: PMC10304213
- DOI: 10.1186/s13024-023-00637-0
Anti-amyloid therapies for Alzheimer disease: finally, good news for patients
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Ramanan receives research funding from the NIH and the Mangurian Foundation for Lewy Body disease research, has provided educational content for Medscape, is PI for a clinical trial sponsored by the Alzheimer’s Association, and is a site clinician for clinical trials sponsored by Eisai, the Alzheimer's Treatment and Research Institute at USC, and Transposon Therapeutics, Inc.
Dr. Day is supported by the NIH (K23AG064029, U01AG057195, U19AG032438), the Alzheimer’s Association, and Chan Zuckerberg Initiative; he serves as a consultant for Parabon Nanolabs Inc, as a Topic Editor (Dementia) for DynaMed (EBSCO), and as the Clinical Director of the Anti-NMDA Receptor Encephalitis Foundation (Inc, Canada; uncompensated); he is the co-Project PI for a clinical trial in anti-NMDAR encephalitis, which receives support from Horizon Pharmaceuticals; he has developed educational materials for PeerView Media, Inc, and Continuing Education Inc; he owns stock in ANI pharmaceuticals; and his institution has received support from Eli Lilly for his development and participation in an educational event promoting early diagnosis of symptomatic Alzheimer disease.
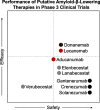
Figures
References
-
- van Dyck CH, Swanson CJ, Aisen P, Bateman RJ, Chen C, Gee M, et al. Lecanemab in Early Alzheimer's Disease. New England J Med. 2022. N Engl J Med . 2023;388(1):9–21. 10.1056/NEJMoa2212948. - PubMed
-
- Company ELa. Lilly's Donanemab significantly slowed cognitive and functional decline in phase 3 study of early alzheimer’s disease. 2023. Available from: https://investor.lilly.com/news-releases/news-release-details/lillys-don.... Accessed 20 May 2023.
-
- McDade E, Cummings JL, Dhadda S, Swanson CJ, Reyderman L, Kanekiyo M, et al. Lecanemab in patients with early Alzheimer's disease: detailed results on biomarker, cognitive, and clinical effects from the randomized and open-label extension of the phase 2 proof-of-concept study. Alzheimer’s Res Therapy. 2022;14(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s13195-022-01124-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

