ARPC5 deficiency leads to severe early-onset systemic inflammation and mortality
- PMID: 37382373
- PMCID: PMC10387347
- DOI: 10.1242/dmm.050145
ARPC5 deficiency leads to severe early-onset systemic inflammation and mortality
Abstract
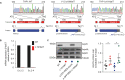
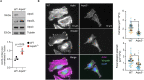
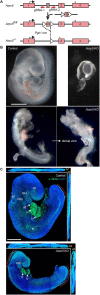
The Arp2/3 complex drives the formation of branched actin networks that are essential for many cellular processes. In humans, the ARPC5 subunit of the Arp2/3 complex is encoded by two paralogous genes (ARPC5 and ARPC5L) with 67% identity. Through whole-exome sequencing, we identified a biallelic ARPC5 frameshift variant in a female child who presented with recurrent infections, multiple congenital anomalies, diarrhea and thrombocytopenia, and suffered early demise from sepsis. Her consanguineous parents also had a previous child who died with similar clinical features. Using CRISPR/Cas9-mediated approaches, we demonstrate that loss of ARPC5 affects actin cytoskeleton organization and function in vitro. Homozygous Arpc5-/- mice do not survive past embryonic day 9 owing to developmental defects, including loss of the second pharyngeal arch, which contributes to craniofacial and heart development. Our results indicate that ARPC5 is important for both prenatal development and postnatal immune signaling, in a non-redundant manner with ARPC5L. Moreover, our observations add ARPC5 to the list of genes that should be considered when patients present with syndromic early-onset immunodeficiency, particularly if recessive inheritance is suspected.
Keywords: Actin; Actinopathy; Arp2/3; CRISPR/Cas9; Immunodeficiency.
© 2023. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Ansar, M., Ebstein, F., Ozkoc, H., Paracha, S. A., Iwaszkiewicz, J., Gesemann, M., Zoete, V., Ranza, E., Santoni, F. A., Sarwar, M. T.et al. (2020). Biallelic variants in PSMB1 encoding the proteasome subunit beta6 cause impairment of proteasome function, microcephaly, intellectual disability, developmental delay and short stature. Hum. Mol. Genet. 29, 1132-1143. 10.1093/hmg/ddaa032 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

