Utilization of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in children and adolescents in China: a real-world study
- PMID: 37383395
- PMCID: PMC10293789
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1170127
Utilization of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in children and adolescents in China: a real-world study
Abstract
Background: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) have been widely used in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and obesity in adults, but scientific research about the indication in children and adolescents is scarce. The current study aims to explore the prescriptions of GLP-1RAs in children and adolescents in China and to evaluate its rationality.
Methods: GLP-1RA prescriptions of children and adolescents were retrospectively obtained from the Hospital Prescription Analysis Cooperative Project. The study extracted information on patient's demographic characteristics, monotherapy and combination therapy of GLP-1RAs, and trends in GLP-1RA usage from 2016 to 2021. The rationality of GLP-1RA prescriptions was comprehensively assessed based on the indications approved by China National Medical Products Administration (NMPA), the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Medicines Agency (EMA), Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA), and published randomized controlled trials (RCTs).
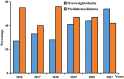
Results: A total of 234 prescriptions from 46 hospitals were included, with a median age of 17 years old. The majority of patients were diagnosed with overweight/obesity or prediabetes/diabetes, accounting for 43.59% and 46.15%, respectively. There were 88 patients on GLP-1RA monotherapy. GLP-1RAs plus metformin was the most common combination therapy (38.89%). 12.39% of patients were found a co-administration with orlistat. The share of overweight/obesity prescriptions increased from 27% in 2016 to 54% in 2021, whereas prediabetes/diabetes prescriptions declined from 55% to 42%. The prescriptions were divided into appropriate and questionable groups according to the diagnosis, and the potentially questionable prescription was related to age (p = 0.017), department visited (p = 0.002), and any hospitalization (p < 0.001).
Conclusions: This study described the prescribing of GLP-1RAs in children and adolescents. Our findings indicated that the utilization of GLP-1RAs has increased from 2016 to 2021. There was a strong basis for administering GLP-1RAs in overweight/obesity and prediabetes/diabetes, whereas the evidence was insufficient in other conditions. It is crucial to demand robust and sustained efforts to enhance the awareness of the safety of utilization of GLP-1RAs in children and adolescents.
Keywords: GLP-1RA; adolescents; children; diabetes; obesity.
Copyright © 2023 Yan, Gong, Jiang, Gao, Guo, Huo, Zhao and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in China (2020 edition). Chin J Pract Internal Med (2021) 41(08):668–95. doi: 10.19538/j.nk2021080106 - DOI
-
- Chen X, Pei Z, Zhang M, Xu Z, Zhao Z, Lu W, et al. . Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) concentrations among children and adolescents with diabetes in middle- and low-income countries, 2010-2019: a retrospective chart review and systematic review of literature. Front Endocrinol (2021) 12:651589. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.651589 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials