Issues and challenges in diabetic neuropathy management: A narrative review
- PMID: 37383599
- PMCID: PMC10294062
- DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i6.741
Issues and challenges in diabetic neuropathy management: A narrative review
Abstract
Diabetic neuropathy (DN) is a devastating disorder with an increasing prevalence globally. This epidemic can pose a critical burden on individuals and com-munities, subsequently affecting the productivity and economic output of a country. With more people living a sedentary lifestyle, the incidence of DN is escalating worldwide. Many researchers have relentlessly worked on ways to combat this devastating disease. Their efforts have given rise to a number of commercially available therapies that can alleviate the symptoms of DN. Unfortunately, most of these therapies are only partially effective. Worse still, some are associated with unfavorable side effects. This narrative review aims to highlight current issues and challenges in the management of DN, especially from the perspective of molecular mechanisms that lead to its progression, with the hope of providing future direction in the management of DN. To improve the approaches to diabetic management, the suggested resolutions in the literature are also discussed in this review. This review will provide an in-depth understanding of the causative mechanisms of DN, apart from the insights to improve the quality and strategic approaches to DN management.
Keywords: Diabetic management; Diabetic medication; Diabetic neuropathy; Pathophysiology.
©The Author(s) 2023. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: No conflict of interest is identified while preparing the manuscript.
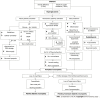
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). 2022. [cited 11 June 2022]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases.... )
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. What is Diabetes? 2022. [cited 11 June 2022]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/diabetes.html .
-
- Dinh Le T, Phi Thi Nguyen N, Thanh Thi Tran H, Luong Cong T, Ho Thi Nguyen L, Do Nhu B, Tien Nguyen S, Van Ngo M, Trung Dinh H, Thi Nguyen H, Trung Nguyen K, Le DC. Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Associated with Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Concentrations Among Newly Diagnosed Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2022;15:35–44. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

