Risk Stratification of Acute-Onset Chest Pain: SVEAT Score Versus HEART and TIMI Scores
- PMID: 37384082
- PMCID: PMC10294122
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.39590
Risk Stratification of Acute-Onset Chest Pain: SVEAT Score Versus HEART and TIMI Scores
Abstract
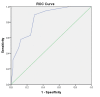
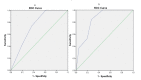
Introduction Acute chest pain is a frequently encountered symptom in the emergency department. Despite the availability of various chest pain risk scores, their effectiveness in identifying low-risk patients suitable for safe and early discharge is inadequate. Moreover, clinical data collected at the initial stage, which has valuable discriminatory ability, is often underutilized. This study aims to assess the effectiveness of the Symptoms, history of Vascular disease, ECG, Age, and Troponin I (SVEAT) score in predicting major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in acute-onset chest pain, compared with the pre-existing History, ECG, Age, Risk factors, and Troponin I (HEART) and Thrombolysis In Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) scores. Methodology This prospective study utilizing non-probability convenience sampling was conducted in the emergency medicine department of a tertiary care hospital in Rawalpindi, Pakistan, for a period of five months from July 2022 to November 2022. The study included patients aged >45 years who presented primarily with chest pain lasting for at least five minutes but less than 24 hours and with a lack of acute ECG changes indicative of ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome (STE-ACS). Patients who were hemodynamically unstable were excluded. All patients were assessed for the calculation of SVEAT, TIMI, and HEART scores. All patients were followed for a period of 30 days to assess the incidence of MACE. Results A total of 60 patients were included. The mean age was 61.5±9.1 years while 31 (51.7%) patients were females. Diabetes was the most prevalent comorbidity (n=32; 53.3%). Regarding MACE, nine (15%) patients developed ACS and underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Two patients (3.3%) experienced heart failure. Six (10%) patients also underwent PCI in the absence of ACS while two (3.3%) patients developed sudden cardiac death. Area-under-curve (AUC) values were determined for SVEAT (0.843; 95%CI: 0.74-0.94), TIMI (0.742; 95%CI: 0.62-0.86), and HEART scores (0.840; 95%CI: 0.74-0.94). A cut-off level of 3.5 SVEAT points obtained a sensitivity of 63.2% and specificity of 75.6% in predicting 30-day MACE. Conclusion SVEAT score potentially lacks the appropriate sensitivity level to predict a significant number of major adverse cardiovascular events compared to contemporary risk stratification scores. Therefore, the SVEAT criteria need re-evaluation as a screening tool for risk assessment in acute chest pain.
Keywords: acute coronary syndrome; chest pain; percutaneous coronary intervention; risk score; risk stratification; timi score.
Copyright © 2023, Shahid et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Prevalence of acute coronary syndrome among patients presenting with chest pain. Sher A, Bashir MA, Humerah S, Khan MR, Raja NS, Hussain I. Pak J Med Health Sci. 2022;16:932–934.
-
- Evaluation of chest pain and acute coronary syndromes. Chang AM, Fischman DL, Hollander JE. Cardiol Clin. 2018;36:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Diagnosis and risk stratification of chest pain patients in the emergency department: focus on acute coronary syndromes. A position paper of the Acute Cardiovascular Care Association. Stepinska J, Lettino M, Ahrens I, et al. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2020;9:76–89. - PubMed
-
- Evaluation of acute chest pain: evolving paradigm of coronary risk scores and imaging. Alderwish E, Schultz E, Kassam Z, Poon M, Coplan N. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2019;20:231–244. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
