AAPM Task Group Report 307: Use of EPIDs for Patient-Specific IMRT and VMAT QA
- PMID: 37384416
- PMCID: PMC11230298
- DOI: 10.1002/mp.16536
AAPM Task Group Report 307: Use of EPIDs for Patient-Specific IMRT and VMAT QA
Abstract
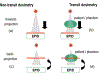
Purpose: Electronic portal imaging devices (EPIDs) have been widely utilized for patient-specific quality assurance (PSQA) and their use for transit dosimetry applications is emerging. Yet there are no specific guidelines on the potential uses, limitations, and correct utilization of EPIDs for these purposes. The American Association of Physicists in Medicine (AAPM) Task Group 307 (TG-307) provides a comprehensive review of the physics, modeling, algorithms and clinical experience with EPID-based pre-treatment and transit dosimetry techniques. This review also includes the limitations and challenges in the clinical implementation of EPIDs, including recommendations for commissioning, calibration and validation, routine QA, tolerance levels for gamma analysis and risk-based analysis.
Methods: Characteristics of the currently available EPID systems and EPID-based PSQA techniques are reviewed. The details of the physics, modeling, and algorithms for both pre-treatment and transit dosimetry methods are discussed, including clinical experience with different EPID dosimetry systems. Commissioning, calibration, and validation, tolerance levels and recommended tests, are reviewed, and analyzed. Risk-based analysis for EPID dosimetry is also addressed.
Results: Clinical experience, commissioning methods and tolerances for EPID-based PSQA system are described for pre-treatment and transit dosimetry applications. The sensitivity, specificity, and clinical results for EPID dosimetry techniques are presented as well as examples of patient-related and machine-related error detection by these dosimetry solutions. Limitations and challenges in clinical implementation of EPIDs for dosimetric purposes are discussed and acceptance and rejection criteria are outlined. Potential causes of and evaluations of pre-treatment and transit dosimetry failures are discussed. Guidelines and recommendations developed in this report are based on the extensive published data on EPID QA along with the clinical experience of the TG-307 members.
Conclusion: TG-307 focused on the commercially available EPID-based dosimetric tools and provides guidance for medical physicists in the clinical implementation of EPID-based patient-specific pre-treatment and transit dosimetry QA solutions including intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) treatments.
Keywords: EPID; EPID QA; IMRT/VMAT QA; electronic portal imaging device; patient-specific EPID QA.
© 2023 The Authors. Medical Physics published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURE STATEMENT
The members of AAPM TG-307 listed below disclose the following potential Conflict(s) of Interest related to subject matter or materials presented in this document.
Jie Shi, PhD, works for Sun Nuclear Corporation (A Mirion Medical Company), and Shannon M. Holmes, PhD, works for Standard Imaging, whose EPID software products, are discussed in this work.
The rest of the authors have no conflict of interest related to subject matter or materials presented in this document.
Figures


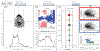



References
-
- Adamson J, Wu Q. Independent verification of gantry angle for pre-treatment VMAT QA using EPID. Phys Med Biol. 2012; 57:6587–6600. - PubMed
-
- Alhazmi A, Gianoli C, Neppl S, et al. A novel approach to EPID-based 3D volumetric dosimetry for IMRT and VMAT QA. Phys Med Biol. 2018; 63:115002. - PubMed
-
- Ansbacher W Three-dimensional portal image-based dose reconstruction in a virtual phantom for rapid evaluation of IMRT plans. Med Phys. 2006; 33:3369–3382. - PubMed
-
- Antonuk L Future EPID technology and applications. Med Phys. 2016; 43:3745–3745.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

