Abemaciclib Is Effective in Palbociclib-Resistant Hormone Receptor-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancers
- PMID: 37384539
- PMCID: PMC10592446
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-0705
Abemaciclib Is Effective in Palbociclib-Resistant Hormone Receptor-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancers
Abstract
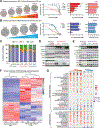
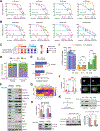
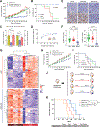
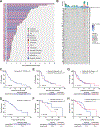
Cyclin-dependent kinases 4/6 inhibitor (CDK4/6i) plus endocrine therapy (ET) is standard of care for patients with hormone receptor (HR)-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer (MBC). However, resistance to CDK4/6is plus ET remains a clinical problem with limited therapeutic options following disease progression. Different CDK4/6is might have distinct mechanisms of resistance, and therefore using them sequentially or targeting their differentially altered pathways could delay disease progression. To understand pathways leading to resistance to the CDK4/6is palbociclib and abemaciclib, we generated multiple in vitro models of palbociclib-resistant (PR) and abemaciclib-resistant (AR) cell lines as well as in vivo patient-derived xenografts (PDX) and ex vivo PDX-derived organoids (PDxO) from patients who progressed on CDK4/6i. PR and AR breast cancer cells exhibited distinct transcriptomic and proteomic profiles that sensitized them to different classes of inhibitors; PR cells upregulated G2-M pathways and responded to abemaciclib, while AR cells upregulated mediators of the oxidative phosphorylation pathway (OXPHOS) and responded to OXPHOS inhibitors. PDX and organoid models derived from patients with PR breast cancer remained responsive to abemaciclib. Resistance to palbociclib while maintaining sensitivity to abemaciclib was associated with pathway-specific transcriptional activity but was not associated with any individual genetic alterations. Finally, data from a cohort of 52 patients indicated that patients with HR-positive/HER2-negative MBC who progressed on palbociclib-containing regimens can exhibit a meaningful overall clinical benefit from abemaciclib-based therapy when administered after palbociclib. These findings provide the rationale for clinical trials evaluating the benefit of abemaciclib treatment following progression on a prior CDK4/6i.
Significance: Palbociclib-resistant breast cancers respond to abemaciclib and express pathway-specific signatures of sensitivity, providing a biomarker-driven therapeutic option for patients with metastatic breast cancer following disease progression on cyclin-dependent kinases 4/6 inhibitors.
©2023 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest:
J. Navarro-Yepes: None.
N.M. Kettner: None.
X. Rao: None.
C.S. Bishop: None
T. Bui: None.
H.F. Wingate: None.
A.S. Raghavendra: None.
Y. Wang: None.
J. Wang: None.
A. Sahin: None.
F. Meric-Bernstam: AbbVie, Aduro BioTech Inc., Aileron Therapeutics Inc., Alkermes, AstraZeneca, Black Diamond, Bayer Healthcare Pharmaceutical, Biovica, Calithera Biosciences Inc., Curis Inc., CytomX Therapeutics Inc., Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd., DebioPharm, Ecor1 Capital, eFFECTOR Therapeutics, Eisai, F. Hoffman-La Roche Ltd., FogPharma, GT Apeiron, Genentech Inc., Guardant Health Inc., Harbinger Health, IBM Watson, Immunomedics, Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Inflection Biosciences, Jackson Laboratory, Karyopharm Therapeutics, Kolon Life Science, Klus Pharma, Lengo Therapeutics, Loxo Oncology, Menarini Group, Mersana Therapeutics, Novartis, OnCusp Therapeutics, OrigiMed, PACT Pharma, Parexel International, Pfizer Inc., Protai Bio Ltd, Puma Biotechnology Inc., Samsung Bioepis, Sanofi, Seattle Genetics Inc., Silverback Therapeutics, Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Takeda Pharmaceutical, Tallac Therapeutics, Tyra Biosciences, Xencor, Zentalis, Zymeworks
K.K. Hunt: Armada Health, AstraZeneca, Cairn Surgical, Eli Lilly & Co, Lumicell.
S. Damodaran: EMD Serono, Guardant Health, Novartis, Pfizer, Sermonix, Taiho.
D. Tripathy: AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Gilead, Novartis, OncoPep, Pfizer, Polyphor, Personalis, Puma Biotechnology, Sermonix, Stemline-Menarini.
K. Keyomarsi: Apeiron, BluePrint, REPARE, Schrodinger and Novartis.
Figures


Comment in
-
Distinct Mechanisms of Resistance to CDK4/6 Inhibitors Require Specific Subsequent Treatment Strategies: One Size Does Not Fit All.Cancer Res. 2023 Oct 2;83(19):3165-3167. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-2608. Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37779425
References
-
- Andre F, Ciruelos E, Rubovszky G, Campone M, Loibl S, Rugo HS, et al. Alpelisib for PIK3CA-Mutated, Hormone Receptor-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer. N Engl J Med 2019;380:1929–40 - PubMed
-
- Cristofanilli M, Turner NC, Bondarenko I, Ro J, Im SA, Masuda N, et al. Fulvestrant plus palbociclib versus fulvestrant plus placebo for treatment of hormone-receptor-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer that progressed on previous endocrine therapy (PALOMA-3): final analysis of the multicentre, double-blind, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 2016;17:425–39 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

