Treatment of Early Undifferentiated Chronic Monoarthritis of the Wrist by Arthroscopic Wrist Synovectomy Combined with Partial Denervation
- PMID: 37385950
- PMCID: PMC10350389
- DOI: 10.1111/os.13762
Treatment of Early Undifferentiated Chronic Monoarthritis of the Wrist by Arthroscopic Wrist Synovectomy Combined with Partial Denervation
Abstract
Objective: Undifferentiated chronic monosecarthritis (UCMA) is a group of inflammatory joint diseases that has the potential to progress to other diseases and can seriously affect patients' quality of life. There is yet no unified consensus regarding treatment of UCMA. This study aimed to investigate the efficacy of arthroscopic synovectomy combined with partial wrist denervation in treating Larsen 1-3 UCMA.
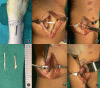
Methods: In this case series, we reviewed 14 patients with UCMA treated by arthroscopic synovectomy combined with partial denervation from February 2017 to June 2020. The mean duration of symptoms was 17.4 months (range, 4-60 months), and the mean follow-up was 13.3 months (range, 6-23 months). The anterior and posterior interosseous nerves were severed at the distal forearm, and the radiocarpal, midcarpal, and distal radial ulnar joint synovial membranes were arthroscopically resected at the wrist. The clinical evaluation indices included the visual analogue scale score (VAS) for pain, grip strength, range of (active) motion of the wrist, total active motion, and Mayo wrist score. Larsen's scoring method was used as the imaging evaluation index.
Results: At the last follow-up, significant clinical improvements were observed in the visual analogue scale (VAS) score for pain (6.0 (5.0-6.3) vs 1.0 (1.0-2.3), P = 0.001) and Mayo wrist score (42.1 ± 9.7 vs 61.8 ± 12.3, P < 0.0001). No significant changes were found in grip strength (15.9 ± 4.5 vs 16.6 ± 4.7, P = 0.230) or the flexion-extension arc (58.9 ± 39.0 vs 64.3 ± 36.5, P = 0.317), although the mean and median did show positive changes. Among the three patients who showed progress in imaging, there was no significant difference in their pain and functional scores compared to those who did not progress. One patient underwent total wrist fusion 17 months after the operation.
Conclusion: Arthroscopic wrist synovectomy combined with partial wrist denervation can provide sustained pain relief and functional recovery for patients with Larsen 1-3 UCMA.
Keywords: Arthritis; Arthroscopy; Denervation; Synovectomy; Undifferentiated.
© 2023 The Authors. Orthopaedic Surgery published by Tianjin Hospital and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors. None of the authors has a financial interest in any of the products or devices mentioned in this article.
Figures



References
-
- Quinn MA, Green MJ, Marzo‐Ortega H, Proudman S, Karim Z, Wakefield RJ, et al. Prognostic factors in a large cohort of patients with early undifferentiated inflammatory arthritis after application of a structured management protocol. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(11):3039–45. 10.1002/art.11269 - DOI - PubMed
-
- van Aken J, van Dongen H, le Cessie S, Allaart CF, Breedveld FC, Huizinga TW. Comparison of long term outcome of patients with rheumatoid arthritis presenting with undifferentiated arthritis or with rheumatoid arthritis: an observational cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65(1):20–5. 10.1136/ard.2005.038471 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Verpoort KN, van Dongen HA, llaart CF, Toes RE, Breedveld FC, Huizinga TW. Undifferentiated arthritis—disease course assessed in several inception cohorts. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2004;22(5 Suppl 35):S12–7. - PubMed
-
- Horton SC, Tan AL, Wakefield RJ, Freeston JE, Buch MH, Emery P. Ultrasound‐detectable grey scale synovitis predicts future fulfilment of the 2010 ACR/EULAR RA classification criteria in patients with new‐onset undifferentiated arthritis. RMD Open. 2017;3(1):e000394. 10.1136/rmdopen-2016-000394 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

